


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 3-11-2021
Date: 15-10-2021
Date: 2-1-2022
|
Although more than 300 amino acids occur in nature, proteins are synthesized almost exclusively from the set of 20 L-α amino acids encoded by nucleotide triplets called codons (see Table 1).
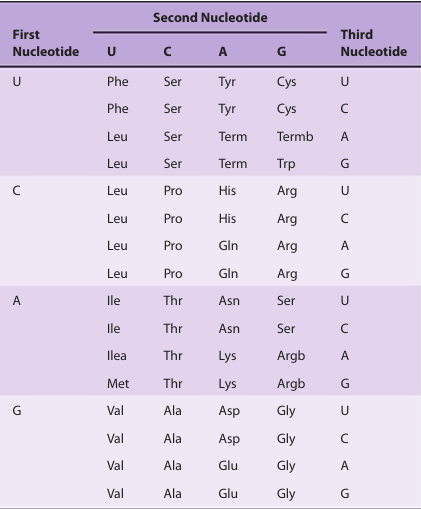
table1. The Genetic Codea (Codon Assignments in Mammalian Messenger RNAs)
While the three-letter genetic code could potentially accommodate more than 20 amino acids, the genetic code is redundant since several amino acids are specified by multiple codons. Scientists frequently represent the sequences of peptides and proteins using one- and three-letter abbreviations for each amino acid (Table 2). The R groups of amino acids may be either hydrophilic or hydrophobic (Table 3); properties that affect their location in a protein’s mature folded conformation . Some proteins contain additional amino acids that arise by the posttranslational modification of an amino acid already present in a peptide. Examples include the conversion of peptidyl proline and peptidyl lysine to 4-hydroxyproline and 5-hydroxylysine; the conversion of peptidyl glutamate to γ-carboxyglutamate; and the methylation, formylation, acetylation, prenylation, and phosphorylation of certain aminoacyl residues. These modifications significantly extend the functional diversity of proteins by altering their solubility, stability, catalytic activity, and interaction with other proteins.
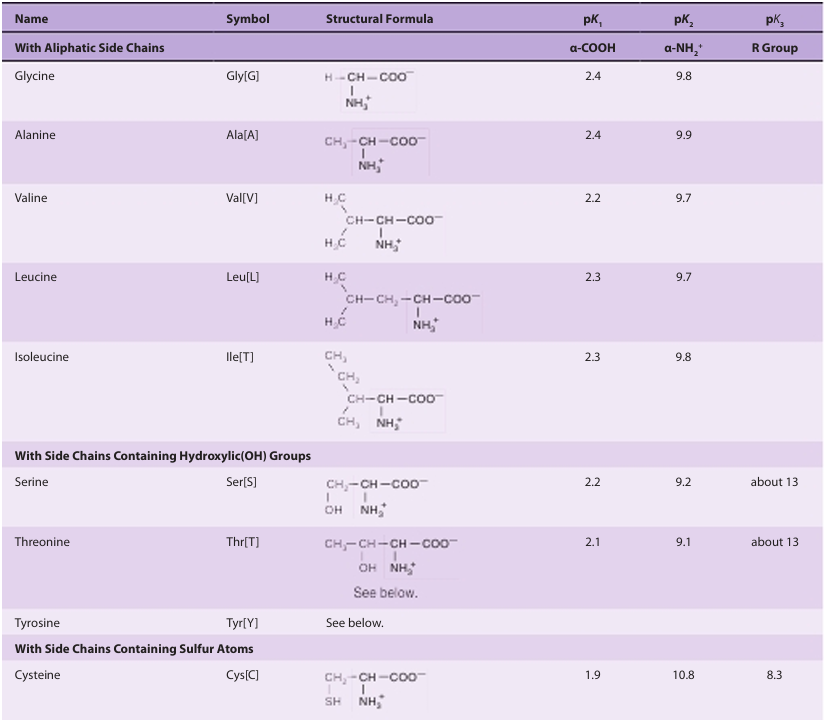
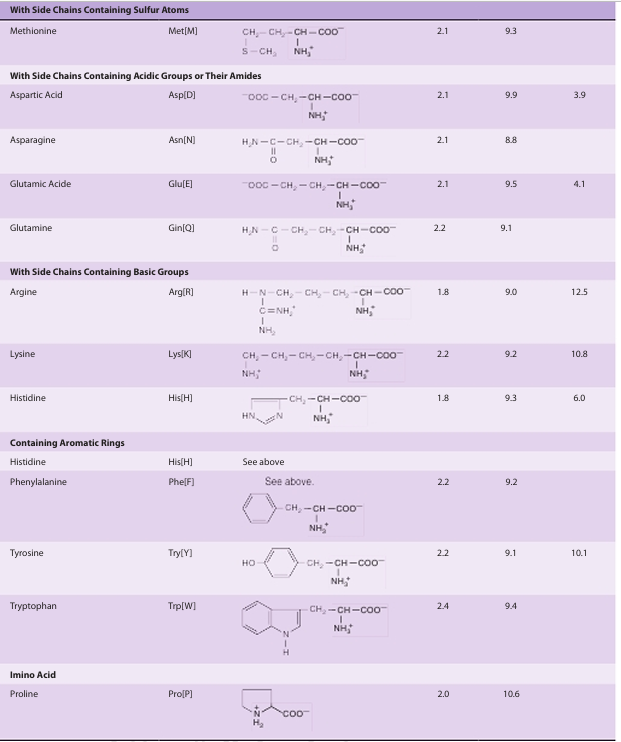
table2. L-α-Amino Acids Present in Proteins (Continued)
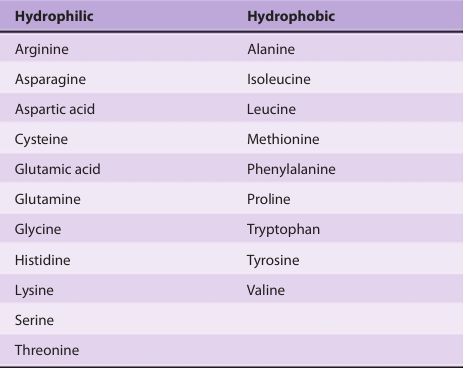
table3. Hydrophilic & Hydrophobic Amino Acids



|
|
|
|
للعاملين في الليل.. حيلة صحية تجنبكم خطر هذا النوع من العمل
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"ناسا" تحتفي برائد الفضاء السوفياتي يوري غاغارين
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|