


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
أقرأ أيضاً
التاريخ: 20-11-2019
التاريخ: 22-11-2015
التاريخ: 2024-12-21
التاريخ: 13-8-2018
|
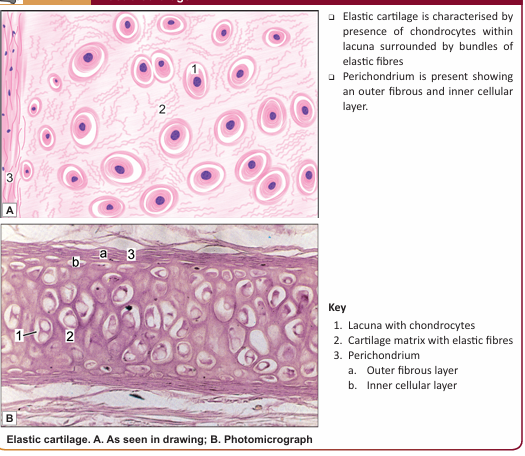
Elastic cartilage (or yellow fibrocartilage) is similar in many ways to hyaline cartilage.
The main difference between hyaline cartilage and elastic cartilage is that instead of collagen fibres, the matrix contains numerous elastic fibres that form a network. The fibres are difficult to see in haematoxylin and eosin stained sections, but they can be clearly visualised if special methods for staining elastic fibres are. The surface of elastic cartilage is covered by perichondrium. Elastic cartilage possesses greater flexibility than hyaline cartilage and readily recovers its shape after being deformed.
Distribution of Elastic Cartilage
- It forms the 'skeletal' basis of the auricle (or pinna) and of the lateral part of the external acoustic meatus.
- The wall of the medial part of the auditory tube is made of elastic cartilage.
- The epiglottis and two small laryngeal cartilages (corniculate and cuneiform) consist of elastic cartilage. The apical part of the arytenoid cartilage contains elastic fibres but the major portion of it is hyaline.
Note that all the sites mentioned above are concerned either with the production or reception of sound.



|
|
|
|
للعاملين في الليل.. حيلة صحية تجنبكم خطر هذا النوع من العمل
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"ناسا" تحتفي برائد الفضاء السوفياتي يوري غاغارين
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|