
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Ionic conductivity
المؤلف:
Richard Feynman, Robert Leighton and Matthew Sands
المصدر:
The Feynman Lectures on Physics
الجزء والصفحة:
Volume I, Chapter 43
2024-06-06
1868
We now apply our results to a special case. Suppose we have a gas in a vessel in which there are also some ions—atoms or molecules with a net electric charge. We show the situation schematically in Fig. 43–2. If two opposite walls of the container are metallic plates, we can connect them to the terminals of a battery and thereby produce an electric field in the gas. The electric field will result in a force on the ions, so they will begin to drift toward one or the other of the plates. An electric current will be induced, and the gas with its ions will behave like a resistor. By computing the ion flow from the drift velocity, we can compute the resistance. We ask, specifically: How does the flow of electric current depend on the voltage difference V that we apply across the two plates?
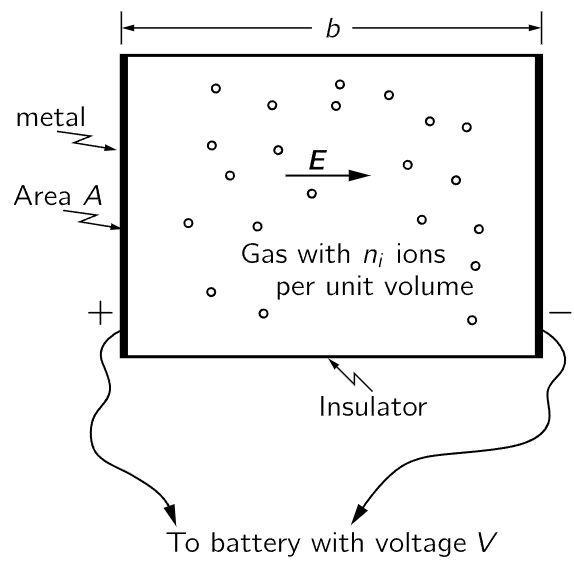
Fig. 43–2. Electric current from an ionized gas.
We consider the case that our container is a rectangular box of length b and cross-sectional area A (Fig. 43–2). If the potential difference, or voltage, from one plate to the other is V, the electric field E between the plates is V/b. (The electric potential is the work done in carrying a unit charge from one plate to the other. The force on a unit charge is E. If E is the same everywhere between the plates, which is a good enough approximation for now, the work done on a unit charge is just Eb, so V=Eb.) The special force on an ion of the gas is qE, where q is the charge on the ion. The drift velocity of the ion is then μ times this force, or
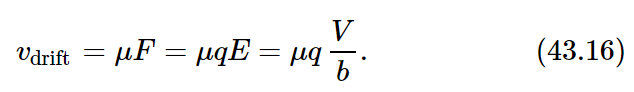
An electric current I is the flow of charge in a unit time. The electric current to one of the plates is given by the total charge of the ions which arrive at the plate in a unit of time. If the ions drift toward the plate with the velocity vdrift, then those which are within a distance (vdrift⋅T) will arrive at the plate in the time T. If there are ni ions per unit volume, the number which reach the plate in the time T is (ni⋅A⋅vdrift⋅T). Each ion carries the charge q, so we have that
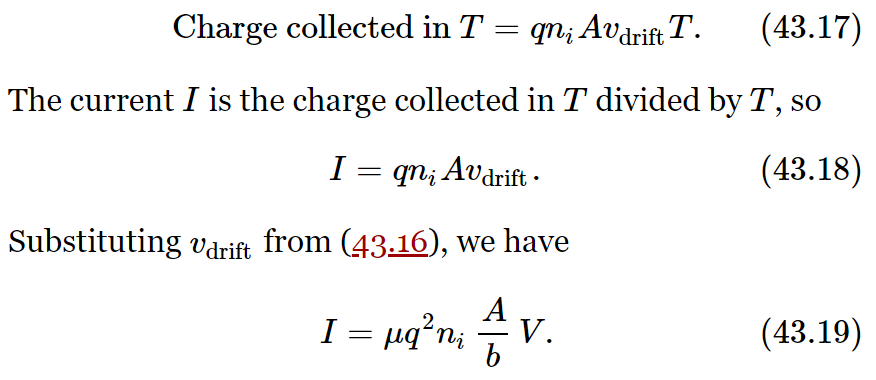
We find that the current is proportional to the voltage, which is just the form of Ohm’s law, and the resistance R is the inverse of the proportionality constant:

We have a relation between the resistance and the molecular properties ni, q, and μ, which depends in turn on m and τ. If we know ni and q from atomic measurements, a measurement of R could be used to determine μ, and from μ also τ.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكهربائية
الاكثر قراءة في الكهربائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















