


 Grammar
Grammar
 Tenses
Tenses
 Present
Present
 Past
Past
 Future
Future
 Parts Of Speech
Parts Of Speech
 Nouns
Nouns
 Verbs
Verbs
 Adverbs
Adverbs
 Adjectives
Adjectives
 Pronouns
Pronouns
 Pre Position
Pre Position
 Preposition by function
Preposition by function 
 Preposition by construction
Preposition by construction
 Conjunctions
Conjunctions
 Interjections
Interjections
 Grammar Rules
Grammar Rules
 Linguistics
Linguistics
 Semantics
Semantics
 Pragmatics
Pragmatics
 Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension|
Read More
Date: 2023-10-12
Date: 2025-02-14
Date: 21-1-2022
|
function (n./v.)
One of the most widely used terms in LINGUISTICS, with a correspondingly wide range of meanings. There are four main areas of application. The relationship between a linguistic FORM and other parts of the linguistic pattern or SYSTEM in which it is used. In GRAMMAR, for example, the NOUN PHRASE can ‘function’ in CLAUSE structure as SUBJECT, OBJECT, COMPLEMENT, etc., these roles being defined distributionally. Syntactic functions (or ‘syntactic relations’ or ‘grammatical relations’) of this kind are a major feature of several MODELS of linguistic analysis, including the approaches of the PRAGUE SCHOOL, GLOSSEMATICS, RELATIONAL GRAMMAR and LEXICAL FUNCTIONAL GRAMMAR, and the terms functional analysis and functional linguistics have been used to characterize theories which treat the notion of function as central. In GOVERNMENT-BINDING THEORY and PHRASE-STRUCTURE grammars, grammatical functions (GF) are notions defined in terms of the position in clause structure of a constituent; in relational and lexical functional grammars they are PRIMITIVES. Functional explanations of grammatical phenomena are also to be found in COMMUNICATIVE and DISCOURSE-based grammars. More specifically, the term functional is used of an ELEMENT which is DISTINCTIVE, or CONTRASTIVE, within a language system, as in one definition of PHONOLOGY as functional phonetics.
The use made of a linguistic contrast in a SYSTEM is sometimes referred to as its functional load or yield. The term is usually used with reference to phonology, where in English, for example, the contrast between /p/ and /b/ would be said to have a higher functional load than between 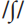 and
and 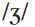 : the former contrast distinguishes many MINIMAL PAIRS, whereas the latter contrast distinguishes only a few. Several criteria are used in making such quantitative judgements, such as the position within a WORD at which the contrast is found, and the frequency of occurrence of the words in the language.
: the former contrast distinguishes many MINIMAL PAIRS, whereas the latter contrast distinguishes only a few. Several criteria are used in making such quantitative judgements, such as the position within a WORD at which the contrast is found, and the frequency of occurrence of the words in the language.
The role language plays in the context of society or the individual is also referred to by the term ‘function’ (social function). For example, language is used (‘functions’) to communicate ideas, to express attitudes, and so on. It may also be used to identify specific SOCIOLINGUISTIC situations, such as informality or intimacy, or VARIETIES of language such as science and law: in such cases, one might talk, for instance, of the ‘function’ of scientific language being to express a certain mode of experience in a certain way, and so on. Several detailed classifications of the social functions of language have been made, especially in HALLIDAYAN linguistics, and in relation to PRAGMATICS and the theory of SPEECH ACTS. The traditional classification of SENTENCE functions falls between grammatical and SPEECH-ACT theory: sentences are said to ‘function’ as STATEMENTS, QUESTIONS, COMMANDS, etc. In narratology, the term is used in the analysis of plots for a type of action performed by one or more types of character, such as ‘Villain harms member of family’.
In FORMALIZED analyses, function is often used in its general mathematical sense: a relation which matches each object in its DOMAIN with exactly one value.
|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مؤتمر ذاكرة الألم في العراق يشهد انعقاد الجلسة البحثية الافتتاحية
|
|
|