

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Fibrin Meshwork Formation : Formation of γ-carboxyglutamate residues
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
6-1-2022
2474
Fibrin Meshwork Formation : Formation of γ-carboxyglutamate residues
γ-Carboxylation is a posttranslational modification in which 9–12 glutamate residues (at the amino [N]-terminus of the target protein) get carboxylated at the γ carbon, thereby forming Gla residues. The process occurs in the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) of the liver.
1. γ-Carboxylation: This carboxylation reaction requires a protein substrate, oxygen (O2), carbon dioxide (CO2), γ-glutamyl carboxylase, and the hydroquinone form of vitamin K as a coenzyme (Fig. 1). In the reaction, the hydroquinone form of vitamin K gets oxidized to its epoxide form as O2 is reduced to water. [Note: Dietary vitamin K, a fat-soluble vitamin , is reduced from the quinone form to the hydroquinone coenzyme form by vitamin K reductase (Fig. 2).]
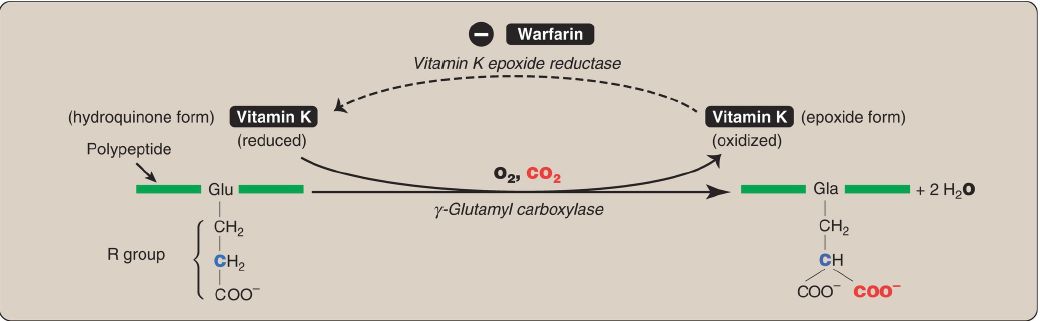
Figure 1: γ-Carboxylation of a glutamate (Glu) residue to γ-carboxyglutamate (Gla) by vitamin K–requiring γ-glutamyl carboxylase. The γ carbon is shown in blue. O2 = oxygen; CO2 = carbon dioxide.
Figure 2: The vitamin K cycle. VKOR = vitamin K epoxide reductase.
2. Inhibition by warfarin: The formation of Gla residues is sensitive to inhibition by warfarin, a synthetic analog of vitamin K that inhibits the enzyme vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR). The reductase, an integral protein of the RER membrane, is required to regenerate the functional hydroquinone form of vitamin K from the epoxide form generated in the γ-carboxylation reaction. Thus, warfarin is an anticoagulant that inhibits clotting by functioning as a vitamin K antagonist. Warfarin salts are used therapeutically to limit clot formation.
[Note: Warfarin is used commercially as a pest control agent such as in rat poison. It was developed by the Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation, hence the name.]
Genetic differences (genotypes) in the gene for catalytic subunit 1 of VKOR (VKORC1) influence patient response to warfarin. For example, a polymorphism in the promoter region of the gene decreases gene expression, resulting in less VKOR being made, thereby necessitating a lower dose of warfarin to achieve a therapeutic level. Polymorphisms in the cytochrome P450 enzyme (CYP2C9) that metabolizes warfarin are also known. In 2010, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration added a genotypebased dose table to the warfarin label (package insert). The influence of genetics on an individual’s response to drugs is known as pharmacogenetics.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















