


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 5-10-2021
Date: 10-9-2021
Date: 29-12-2021
|
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate dephosphorylation in gluconeogenesis
Hydrolysis of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate by fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase,found in the liver and kidneys, bypasses the irreversible phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) reaction of glycolysis and provides an energetically favorable pathway for the formation of fructose 6-phosphate (Fig. 1). This reaction is an important regulatory site of gluconeogenesis.
Figure 1: Dephosphorylation of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. AMP = adenosine monophosphate; = phosphate.
1. Regulation by intracellular energy levels: Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase is inhibited by a rise in the adenosine monophosphate (AMP)/ATP ratio, which signals a low-energy state in the cell. Conversely, low AMP and high ATP levels stimulate gluconeogenesis, an energy-requiring pathway.
2. Regulation by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate: Fructose 1,6- bisphosphatase is inhibited by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, an allosteric effector whose concentration is influenced by the insulin/glucagon ratio. When glucagon is high, the effector is not made by hepatic PFK-2 , and thus, the phosphatase is active (Fig. 2 ). [Note: The signals that inhibit (low energy, high fructose 2,6-bisphosphate) or activate (high energy, low fructose 2,6-bisphosphate) gluconeogenesis have the opposite effect on glycolysis, providing reciprocal control of the pathways that synthesize and oxidize glucose .]
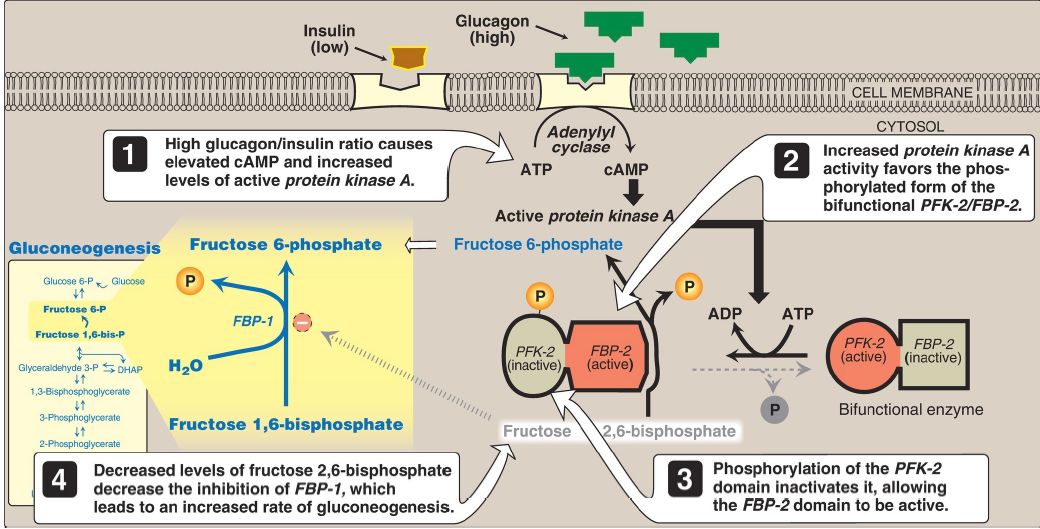
Figure 2: Effect of elevated glucagon on the intracellular concentration of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in the liver. AMP and ADP = adenosine mono- and diphosphates; cAMP = cyclic AMP; PFK-2 = phosphofructokinase-2; FBP-2 =fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase; FBP-1 = fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase; and =phosphate.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|