

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Monosaccharides
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
15-9-2021
1993
Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides (Fig. 1) containing an aldehyde group are called aldoses, and those with a keto group are called ketoses. Disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides consist of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds. Compounds with the same chemical formula but different structures are called isomers. Two monosaccharide isomers differing in configuration around one specific carbon atom (not the carbonyl carbon) are defined as epimers. In enantiomers (mirror images), the members of the sugar pair are designated as D- and L-isomers.
When the aldehyde group on an acyclic sugar gets oxidized as a chromogenic agent gets reduced, that sugar is a reducing sugar. When a sugar cyclizes, an anomeric carbon is created from the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde or keto group. The sugar can have two configurations, forming α or β anomers. A sugar can have its anomeric carbon linked to an –NH2 or an –OH group on another structure through N- and O-glycosidic bonds, respectively. Salivary α-amylase initiates digestion of dietary polysaccharides (for example, starch or glycogen), producing oligosaccharides. Pancreatic α-amylase continues the process. The final digestive processes occur at the mucosal lining of the small intestine.
Several disaccharidases (for example, lactase [β-galactosidase], sucrase, isomaltase, and maltase) produce monosaccharides (glucose, galactose, and fructose). These enzymes are transmembrane proteins of the luminal brush border of intestinal mucosal cells (enterocytes). Absorption of the monosaccharides requires specific transporters. If carbohydrate degradation is deficient (as a result of heredity, disease, or drugs that injure the intestinal mucosa), undigested carbohydrate will pass into the large intestine, where it can cause osmotic diarrhea. Bacterial fermentation of the material produces large volumes of carbon dioxide and hydrogen gas, causing abdominal cramps, diarrhea, and flatulence. Lactose intolerance, primarily caused by the age-dependent loss of lactase (adult-type hypolactasia), is by far the most common of these deficiencies.
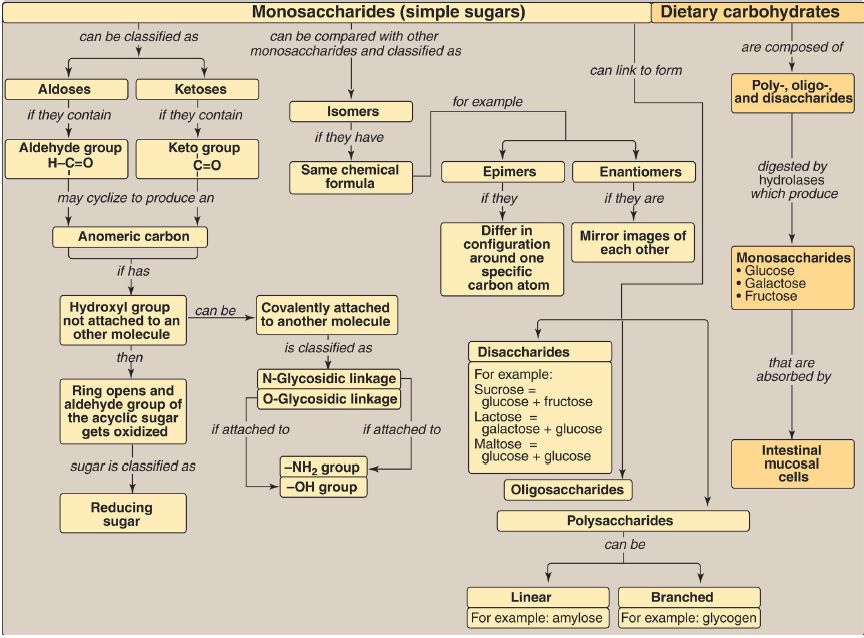
Figure 1: Key concept map for the classification and structure of monosaccharides and the digestion of dietary carbohydrates.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















