

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Allosteric Enzymes
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
7-9-2021
2774
Allosteric Enzymes
The regulation of the reaction velocity of enzymes is essential if an organism is to coordinate its numerous metabolic processes. The rates of most enzymes are responsive to changes in substrate concentration, because the intracellular level of many substrates is in the range of the Km. Thus, an increase in substrate concentration prompts an increase in reaction rate, which tends to return the concentration of substrate toward normal. In addition, some enzymes with specialized regulatory functions respond to allosteric effectors and/or covalent modification or they show altered rates of enzyme synthesis (or degradation) when physiologic conditions are changed.
Allosteric enzymes are regulated by molecules called effectors that bind noncovalently at a site other than the active site. These enzymes are almost always composed of multiple subunits, and the regulatory (allosteric) site that binds the effector is distinct from the substrate-binding site and may be located on a subunit that is not itself catalytic. Effectors that inhibit enzyme activity are termed negative effectors, whereas those that increase enzyme activity are called positive effectors. Positive and negative effectors can affect the affinity of the enzyme for its substrate (K0.5), modify the maximal catalytic activity of the enzyme (Vmax), or both (Fig. 1). [Note:Allosteric enzymes frequently catalyze the committed step, often the ratelimiting
step, early in a pathway.]
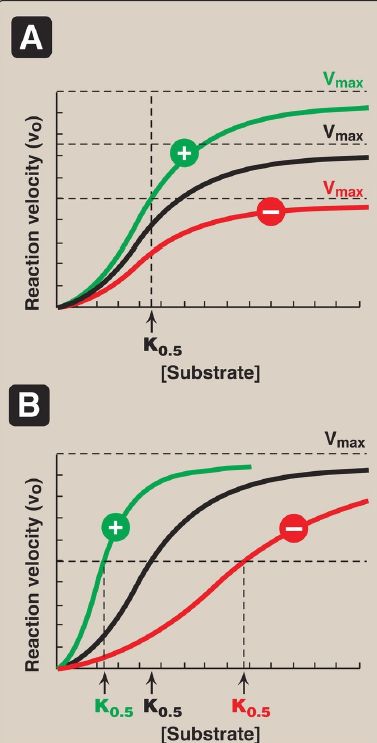
Figure 1: Effects of negative or positive effectors on an allosteric enzyme. A. Maximal velocity (Vmax) is altered. B. The substrate concentration that gives half maximal velocity (K0.5) is altered.
1. Homotropic effectors: When the substrate itself serves as an effector, the effect is said to be homotropic. Most often, an allosteric substrate functions as a positive effector. In such a case, the presence of a substrate molecule at one site on the enzyme enhances the catalytic properties of the other substrate-binding sites. That is, their binding sites exhibit cooperativity. These enzymes show a sigmoidal curve when vo is plotted against substrate concentration, as shown in Figure 1. This contrasts with the hyperbolic curve characteristic of enzymes following Michaelis-Menten kinetics, as previously discussed. [Note: The concept of cooperativity of substrate binding is analogous to the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin .]
2. Heterotropic effectors: The effector may be different from the substrate, in which case the effect is said to be heterotropic. For example, consider the feedback inhibition shown in Figure 2. The enzyme that converts D to E has an allosteric site that binds the end product, G. If the concentration of G increases (for example, because it is not used as rapidly as it is synthesized), the first irreversible step unique to the pathway is typically inhibited. Feedback inhibition provides the cell with appropriate amounts of a product it needs by regulating the flow of substrate molecules through the pathway that synthesizes that product.Heterotropic effectors are commonly encountered. For example, the glycolytic enzyme phosphofructokinase-1 is allosterically inhibited by citrate, which is not a substrate for the enzyme .
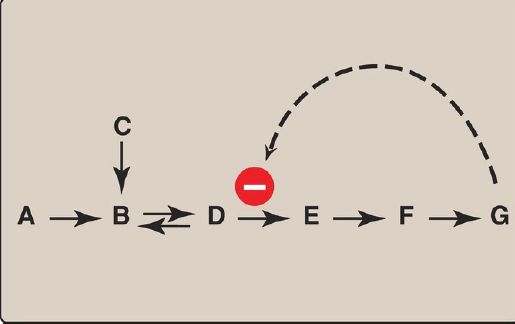
Figure 2: Feedback inhibition of a metabolic pathway.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















