


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 21-1-2021
Date: 11-12-2020
Date: 15-12-2020
|
Potentiometric Biosensors
Changes in ionic concentrations are easily determined by use of ionselective electrodes. This forms the basis for potentiometric biosensors. Many biocatalysed reactions involve charged species, each of which will
Table 1. Biocatalytic reactions that can be used with ion-selective electrode biosensors.
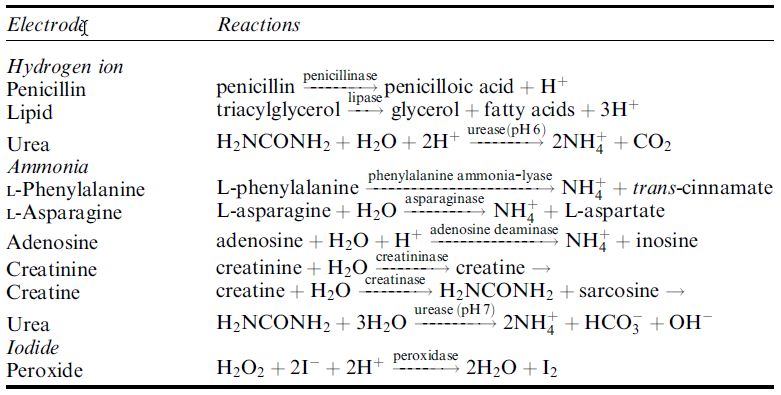

Figure 1. A FET-based potentiometric biosensor.
absorb or release hydrogen ions according to their pKa and the pH of the environment. This allows a relatively simple electronic transduction using the commonest ion selective electrode, the pH electrode. Table 1. shows some biocatalytic reactions that can be utilised in potentiometric biosensors. Potentiometric biosensors can be miniaturised by the use of field effect transistors (FETs).
Ion-selective field effect transistors (ISFETs) are low-cost devices that are in mass production. Figure 1. shows a diagrammatic cross-section through an npn hydrogen ion-responsive ISFET with an approximately 0.025mm2 biocatalytic membrane covering the ion-selective membrane.
The build-up of positive charge on this surface (the gate) repels the positive holes in the p-type silicon, causing a depletion layer and allowing the current to flow. The reference electrode is usually an identical ISFET without any biocatalytic membrane. A major practical problem with the manufacture of such enzyme-linked FETs (ENFETs) is protection of the silicon from contamination by the solution, hence the covering of waterproof encapsulant. Because of their small size, they only require minute amounts of biological material and can be produced in a form whereby they can determine several analytes simultaneously. A further advantage is that they have a more rapid response rate compared with the larger, sluggish ion-selective electrode devices. The enzyme may be immobilised to the silicon nitride gate using polyvinylbutyral deposited by solvent evaporation and cross-linked with glutaraldehyde. Such devices still present fabrication problems such as reproducibility, drift, sensitivity to light and the need for on-chip temperature compensation.
Use of membranes selective for ions other than hydrogen ions, such as ammonium, allows many related biosensors to be constructed. Potentiometric biosensors for DNA have been developed which use anti-DNA monoclonal antibodies conjugated with urease. DNA is bound to a membrane, placed on the electrode and quantified by the change in pH on addition of urea .



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|