


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 9-11-2020
Date: 7-3-2016
Date: 8-3-2016
|
Polarization
In addition to the strength of any radiation and the variation with frequency, the radiation may have another property. Two apparently identical beams of radiation having the same frequency spread and intensity distribution within that spectral range may interact differently with certain materials or devices. From this we may conclude that radiation has another characteristic. This quality is known as polarization. It manifests itself as an orientational quality within the radiation.
The usefulness of polarization as a means of carrying information about a radiating source is sometimes ignored, perhaps as a result of the eye not being directly sensitive to it. However, the simple use of a pair of Polaroid sunglasses reveals that much of the light in nature is polarized to some degree. Rotation of the lenses in front of the eye will demonstrate that the light of the blue sky, light reflected by the sea and light scattered by rough surfaces are all polarized. Measurement of the polarization of the radiation coming from astronomical sources holds much information about the natures of those sources. Its generation may result from scattering processes in a source or by the radiating atoms being in the presence of a magnetic field. Because polarization is essentially an orientational property, its measurement sometimes provides ‘geometric’ information which could not be ascertained by other observational analyses. In stellar measurements, for example, knowledge of the orientations of magnetic fields may be gleaned. In the optical region, the simplest polarimetric measurements can be made by placing a plastic sheet polarizer (similar to that comprising the lenses of Polaroid sunglasses) in the beam and measuring the transmitted intensity as the polarizer is rotated. The larger the relative changes in intensity are, the greater the degree of polarization is. If a wholly polarized beam is generated artificially by using a polarizer (see figure 1) and this beam is then analysed by a rotating polarizer in the usualway, then the measured intensity will fall to zero at a particular orientation of the analysing polarizer. Although the polarization of the radiation coming from astronomical sources is usually very small, its measurement holds much information about the nature of those sources.
All the parameters which are used to describe radiation, i.e. its strength and its variation across the spectrum, together with any polarization properties, carry information about the condition of the source or about the material which scatters the radiation in the direction of the observer or about the matter which is in a direct line between the original source and the observer. If the observer wishes to gain as much knowledge as possible of the outside universe, measurements must be made of all of the properties associated with the electromagnetic radiation.
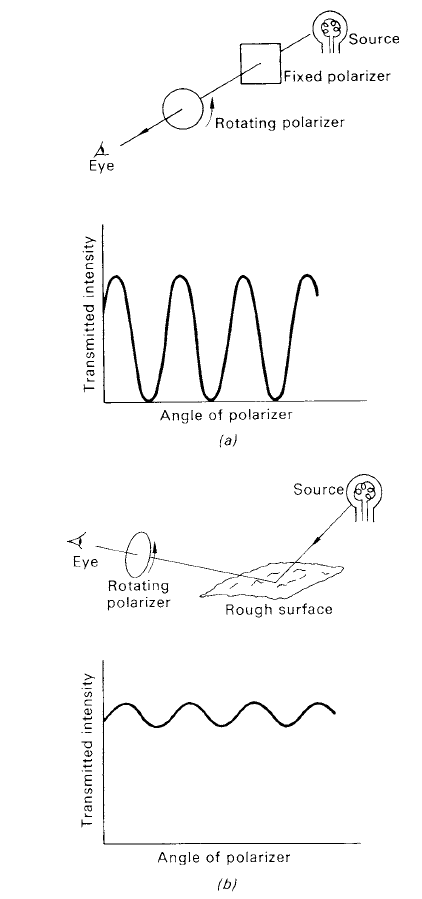
Figure 1. (a) The artificial production and analysis of totally polarized light. (b) The production of partially
polarized light as might occur in nature and its analysis.



|
|
|
|
إجراء أول اختبار لدواء "ثوري" يتصدى لعدة أنواع من السرطان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
دراسة تكشف "سببا غريبا" يعيق نمو الطيور
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يقيم برنامج (صنّاع المحتوى الهادف) لوفدٍ من محافظة ذي قار
|
|
|
|
الهيأة العليا لإحياء التراث تنظّم ورشة عن تحقيق المخطوطات الناقصة
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف يقيم ندوة علمية حول دور الجنوب في حركة الجهاد ضد الإنكليز
|
|
|
|
وفد جامعة الكفيل يزور دار المسنين في النجف الأشرف
|