


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 6-4-2020
Date: 2-2-2020
Date: 7-2-2020
|
The carrier gas plays an important role, and varies in the GC used. Carrier gas must be dry, free of oxygen and chemically inert mobile-phase employed in gas chromatography. Helium is most commonly used because it is safer than, but comprable to hydrogen in efficiency, has a larger range of flow rates and is compatible with many detectors. Nitrogen, argon, and hydrogen are also used depending upon the desired performance and the detector being used. Both hydrogen and helium, which are commonly used on most traditional detectors such as Flame Ionization(FID), thermal conductivity (TCD) and Electron capture (ECD), provide a shorter analysis time and lower elution temperatures of the sample due to higher flow rates and low molecular weight. For instance, hydrogen or helium as the carrier gas gives the highest sensitivity with TCD because the difference in thermal conductivity between the organic vapor and hydrogen/helium is greater than other carrier gas. Other detectors such as mass spectroscopy, uses nitrogen or argon which has a much better advantage than hydrogen or helium due to their higher molecular weights, in which improve vacuum pump efficiency.
All carrier gasses are available in pressurized tanks and pressure regulators, gages and flow meters are used to meticulously control the flow rate of the gas. Most gas supplies used should fall between 99.995% - 99.9995% purity range and contain a low levels (< 0.5 ppm) of oxygen and total hydrocarbons in the tank. The carrier gas system contains a molecular sieve to remove water and other impurities. Traps are another option to keep the system pure and optimum sensitive and removal traces of water and other contaminants. A two stage pressure regulation is required to use to minimize the pressure surges and to monitor the flow rate of the gas. To monitor the flow rate of the gas a flow or pressure regulator was also require onto both tank and chromatograph gas inlet. This applies different gas type will use different type of regulator.The carrier gas is preheated and filtered with a molecular sieve to remove impurities and water prior to being introduced to the vaporization chamber. A carrier gas is typically required in GC system to flow through the injector and push the gaseous components of the sample onto the GC column, which leads to the detector ( see more detail in detector section).
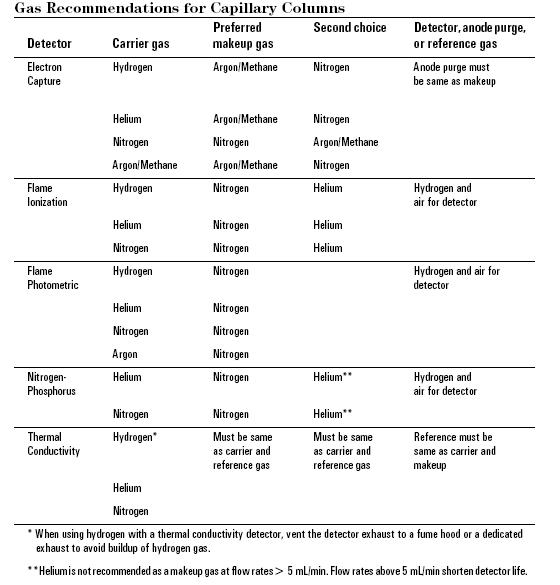
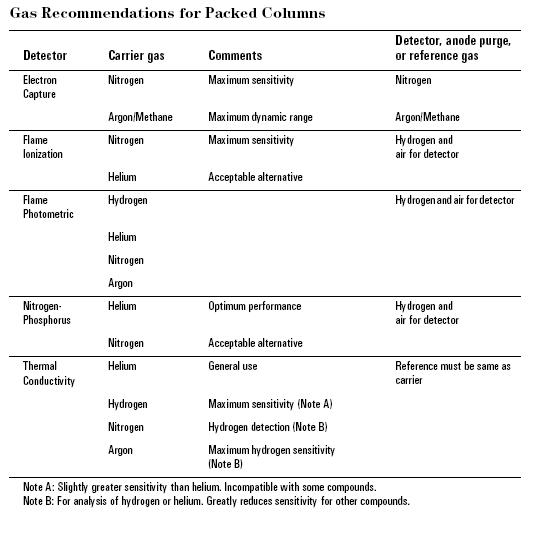
Figure 1. Gas Recommendations for Packed Columns



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|