


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 2-9-2018
Date: 10-6-2019
Date: 10-11-2020
|
The precise physical nature of atoms finally emerged from a series of elegant experiments carried out between 1895 and 1915. The most notable of these achievements was Ernest Rutherford's famous 1911 alpha-ray scattering experiment, which established that
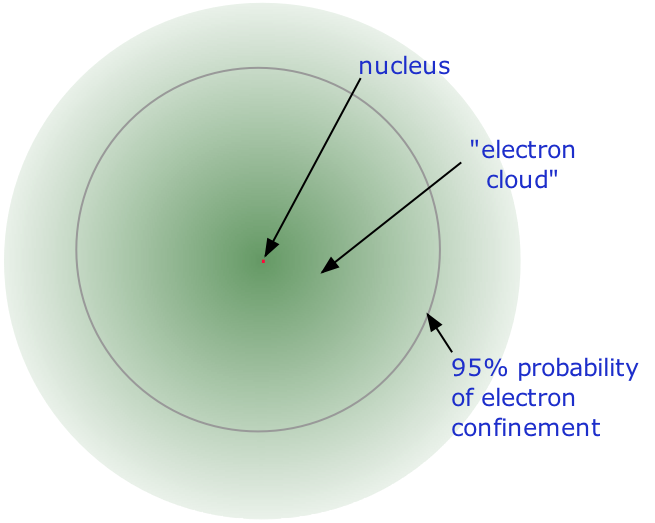
Figure 1.1 : The structure of the nuclear atom with a central nucleus and surrounding electrons.
The nucleus is itself composed of two kinds of particles. Protons are the carriers of positive electric charge in the nucleus; the proton charge is exactly the same as the electron charge, but of opposite sign. This means that in any [electrically neutral] atom, the number of protons in the nucleus (often referred to as the nuclear charge) is balanced by the same number of electrons outside the nucleus. The other nuclear particle is the neutron. As its name implies, this particle carries no electrical charge. Its mass is almost the same as that of the proton. Most nuclei contain roughly equal numbers of neutrons and protons, so we can say that these two particles together account for almost all the mass of the atom.
Because the electrons of an atom are in contact with the outside world, it is possible for one or more electrons to be lost, or some new ones to be added. The resulting electrically-charged atom is called an ion.



|
|
|
|
إجراء أول اختبار لدواء "ثوري" يتصدى لعدة أنواع من السرطان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
دراسة تكشف "سببا غريبا" يعيق نمو الطيور
|
|
|
|
|
|
اللجنة التحضيرية للمؤتمر الحسيني الثاني عشر في جامعة بغداد تعلن مجموعة من التوصيات
|
|
|
|
السيد الصافي يزور قسم التربية والتعليم ويؤكد على دعم العملية التربوية للارتقاء بها
|
|
|
|
لمنتسبي العتبة العباسية قسم التطوير ينظم ورشة عن مهارات الاتصال والتواصل الفعال
|
|
|
|
في جامعة بغداد.. المؤتمر الحسيني الثاني عشر يشهد جلسات بحثية وحوارية
|