


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 24-6-2019
Date: 3-1-2017
Date: 1-1-2017
|
The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms. Another way of saying this is that formal charge results when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom, subtract the nonbonding electrons, and then subtract the number of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure.
Thus, we calculate formal charge as follows:
We can double-check formal charge calculations by determining the sum of the formal charges for the whole structure. The sum of the formal charges of all atoms in a molecule must be zero; the sum of the formal charges in an ion should equal the charge of the ion.
We must remember that the formal charge calculated for an atom is not the actual charge of the atom in the molecule. Formal charge is only a useful bookkeeping procedure; it does not indicate the presence of actual charges.
Example 7.4.1 : Calculating Formal Charge from Lewis Structures Assign formal charges to each atom in the interhalogen ion ICl−4.
Solution
We divide the bonding electron pairs equally for all I–Cl bonds:
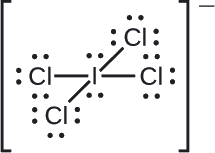
We assign lone pairs of electrons to their atoms. Each Cl atom now has seven electrons assigned to it, and the I atom has eight.
Subtract this number from the number of valence electrons for the neutral atom:
The sum of the formal charges of all the atoms equals –1, which is identical to the charge of the ion (–1).



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تقدم دعوة إلى كلية مزايا الجامعة للمشاركة في حفل التخرج المركزي الخامس
|
|
|