


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 14-10-2020
Date: 25-9-2019
Date: 17-8-2019
|
The joining of a double or triple bond to an alkene reactant having a transferable allylic hydrogen is called an ene reaction. The reverse process is called a retro ene reaction. In the bonding direction the ene reaction is characterized by the redistribution of three pairs of bonding electrons. and may be described by a cycle of three curved arrows. As noted earlier, this bond reorganization involves the overall conversion of a π-bond to a σ-bond (or the opposite in the case of retro ene fragmentation). This is the same bond bookkeeping change exhibited by electrocyclic reactions, but no rings are formed or broken in an ene reaction unless it is intramolecular. The following examples illustrate some typical ene reactions, with equation 3 being an intramolecular ene reaction. Ene reactions are favored when the hydrogen accepting reagent, the "enophile", is electrophilic. This is the case for reactions 1 and 2, which proceed under milder conditions than 3, despite the latter's intramolecular nature.
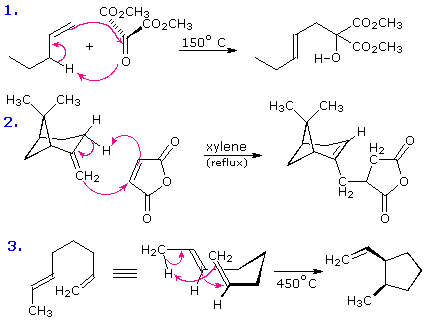


Hydrogen is the most common atom transferred in an ene reaction. Indeed, all the examples shown above involve hydrogen shifts. Other atoms or groups may, however, participate in ene-like transformations. Two such cases will be displayed above by clicking on the diagram. Reaction 4 is drawn as a retro ene reaction, although this has not been demonstrated to be general for all reactions of allylic alcohols with thionyl chloride. Equation 5 illustrates an unusual "magnesium ene reaction" in which a Grignard function moves to a new location before reacting with an electrophilic reagent such as CO2. Because this is an intramolecular ene reaction a new ring is formed. Equation 6 demonstrates that an enol tautomer, even in low concentration, may function as the hydrogen donor in the ene reaction. Equation 7 is one of many examples of Lewis acid catalysis in the ene reaction. A similar acid-catalyzed reaction of simple aldehydes with alkenes to give allylic alcohols, 1,3-diols or 1,3-dioxanes is known as the Prins reaction.
Certain retro ene reactions have proven useful as synthetic transformations.



|
|
|
|
4 أسباب تجعلك تضيف الزنجبيل إلى طعامك.. تعرف عليها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أكبر محطة للطاقة الكهرومائية في بريطانيا تستعد للانطلاق
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أصواتٌ قرآنية واعدة .. أكثر من 80 برعماً يشارك في المحفل القرآني الرمضاني بالصحن الحيدري الشريف
|
|
|