
Preparing Alkyl Halides from Alcohols
 المؤلف:
John McMurry
المؤلف:
John McMurry
 المصدر:
Organic Chemistry
المصدر:
Organic Chemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
9th. p 297
الجزء والصفحة:
9th. p 297
 25-5-2017
25-5-2017
 1275
1275
Preparing Alkyl Halides from Alcohols
The most generally useful method for preparing alkyl halides is to make them from alcohols, which themselves can be obtained from carbonyl compounds. Because of the importance of this process, many different methods have been developed to transform alcohols into alkyl halides. The simplest method is to treat the alcohol with HCl, HBr, or HI. This reaction works best with tertiary alcohols, R3COH. Primary and secondary alcohols react much more slowly and at higher temperatures.

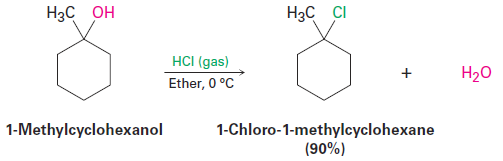
The reaction of HX with a tertiary alcohol is so rapid that it’s often carried out simply by bubbling pure HCl or HBr gas into a cold ether solution of the alcohol. 1-Methylcyclohexanol, for example, is converted into 1-chloro- 1-methylcyclohexane by treatment with HCl.
Primary and secondary alcohols are best converted into alkyl halides by treatment with either thionyl chloride (SOCl2) or phosphorus tribromide (PBr3). These reactions, which normally take place readily under mild conditions, are less acidic and less likely to cause acid-catalyzed rearrangements than the HX method.

As the preceding examples indicate, the yields of these SOCl2 and PBr3 reactions are generally high and other functional groups such as ethers, carbonyls, and aromatic rings don’t usually interfere. Alkyl fluorides can also be prepared from alcohols. Numerous alternative reagents are used for such reactions, including diethylaminosulfur trifluoride [(CH3CH2)2NSF3] and HF in pyridine solvent.

 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


