
Trees
 المؤلف:
Jean-Claude Fournier
المؤلف:
Jean-Claude Fournier
 المصدر:
Graph Theory and Applications
المصدر:
Graph Theory and Applications
 الجزء والصفحة:
44-47
الجزء والصفحة:
44-47
 6-8-2016
6-8-2016
 2337
2337
Definitions and properties
A tree is a connected acyclic graph, where acyclic means without a cycle.A tree is a simple graph (a loop or a double edge would define a cycle).
A path is in particular a tree (see Figure1.1).
Except when explicitly noted otherwise, as with graphs in general, n denotes the number of vertices of a tree and m the number of edges.
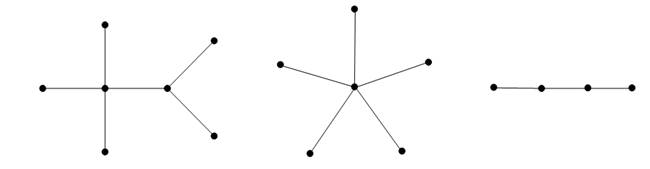
Figure 1.1. Three examples of trees
1-First properties of trees
Proposition 1.1.1. A tree such that n ≥ 2 has at least two vertices of degree one.
Proof. Consider in a given tree a maximal path, that is, a path not contained in a strictly longer path. Let (x0,x1,...,ek,xk) be this path. Since n ≥ 2, we have necessarily k ≥ 1. Let us show that the ends of this path, x0 and xk, which are distinct, are vertices of degree one in the tree. Suppose that vertex x0, for example, is not of degree one and thus has an incident edge f ≠ e1,andlet y be the endvertex of f other than x0.Ifvertex y is one of the vertices of the path, given xj , then there is in the graph a cycle, (xj = y, f,x0,e1,...,xj ), which contradicts the hypothesis that this graph is a tree. If vertex y is not one of the vertices of the path, then this path is not maximal, because it is strictly included in the path (y, f,x0,e1,x1,...,ek,xk). In both cases, there is a contradiction.
Proposition 1.1.2. If G is a tree then m = n − 1.
Proof. Apply inductive reasoning to n. For n =1, we have m =0sincean edge could only be a loop, i.e. a cycle, which is impossible for a tree. Assume n> 1. According to proposition 1.1.1 above, there is in G a vertex of degree one, given x. The subgraph G − x is connected since suppressing a vertex of degree one in a connected graph does not suppress the connectedness property, as is easily verified. In addition, G−x is acyclic because a cycle in G − x would also be a cycle of G, while G, as a tree, is itself acyclic. Thus G/= G − x is a tree and it is possible to apply the induction hypothesis, which gives: mG/= nG/ − 1. As mG/ = mG − 1and nG/ = nG − 1, we can deduce the desired equality: mG = nG − 1.
Proposition 1.1.3. In a tree any two vertices are connected by a unique path.
Proof. The existence of a path linking two vertices of the graph is direct according to the hypothesis of connectedness. To show that it is unique, suppose the existence of two distinct paths linking two vertices x and y. If x = y then one of these two closed paths is of length ≥ 1 and so is a cycle, which contradicts the hypothesis of the tree being acyclic. If x≠ y, the concatenation of the two paths linking x and y is a closed walk. This closed walk is not necessarily a cycle. This is due to the fact that the two paths may share one or more edges (not all of them, since those paths are distinct according to the hypothesis). A small technical work, left to the reader, shows that it is always possible to extract a cycle from the concatenation of the two paths, again a contradiction.
Graph Theory and Applications ,Jean-Claude Fournier, WILEY, page(44-47)
 الاكثر قراءة في نظرية البيان
الاكثر قراءة في نظرية البيان
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


