

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The octet rule
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
الجزء والصفحة:
p36
30-5-2016
1830
The octet rule
The ground state electronic configurations in Table 1.3 map out a pattern illustrating that filled quantum levels provide ‘building blocks’ within the electronic configurations of theheavier elements. Worked example 1.6 emphasized that each noble gas is characterized by having a filled quantum level; with the exception of He, this configuration is of the form ns2 np6. In the early development of bonding models, the octet rule was commonly cited as a means of rationalizing the formation of a particular compound (or ion) which involved an s- or p-block element.
However, the concept of the octet rule is rather limited since it is, strictly, only valid for n = 2. Further, many molecules, especially neutral compounds of boron, simply do not contain enough valence electrons for each atom to be associated with eight electrons. Ions (e.g. Mg+2 and O-2) often exist only in environments in which electrostatic interaction energies compensate for the energies needed to form the ions from atoms.
An atom obeys the octet rule when it gains, loses or shares electrons to give an outer shell containing eight electrons with the configuration ns2 np6.
We have already noted the exception of He, but for n ≥ 3, there is the possibility of apparently expanding the octet . Although the octet rule is still useful at an elementary level, we must bear in mind that it is restricted to a relatively small number of elements.
Worked example: The octet rule and the apparent expansion of the octet
In which of the following covalent compounds is the central atom obeying the octet rule: (a) CH4; (b) H2S; (c) ClF3?
- CH4: A C atom has four valence electrons and forms four covalent bonds by sharing electrons with four Hatoms to give an octet. This can be represented by the Lewis structure:
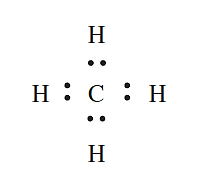
(b) H2S: An S atom has six valence electrons and forms two covalent bonds by sharing electrons with two H atoms to give an octet. The appropriate Lewis structure which shows that S obeys the octet rule in H2S is:


(c) ClF3: A Cl atom has seven valence electrons and should form only one single covalent bond to obtain an octet (e.g. as in Cl2). In ClF3, the octet appears to be expanded:


 الاكثر قراءة في نظريات التآصر الكيميائي
الاكثر قراءة في نظريات التآصر الكيميائي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















