

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Covalent bond distance, covalent radius and van der Waals radius
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
الجزء والصفحة:
p27
8-3-2016
2093
Covalent bond distance, covalent radius and van der Waals radius
Three important definitions are needed before we discuss covalent bonding. The length of a covalent bond (bond distance), d, is the internuclear separation and may be determined experimentally by microwave spectroscopy or diffraction methods (X-ray, neutron or electron diffraction).

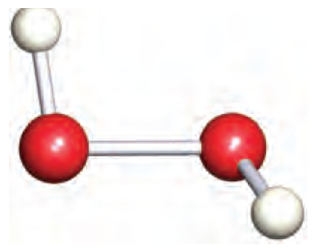
Fig. 1 The structure of hydrogen peroxide, H2O2; O atoms are shown in red.
It is convenient to define the covalent radius, rcov, of an atom: for an atom X, rcov is half of the covalent bond length of a homonuclear X-X single bond. Thus, rcov(S) can be determined from the solid state structure of S8 (Figure 2c) determined by X-ray diffraction methods or, better still, by averaging the values of the bond distances of S-S single bonds found for all the allotropes of sulfur.


Fig. 2 Mass spectrometric traces for (a) atomic Ru and (b) molecular S8; the mass:charge ratio is m/z and in these traces z = 1. (c) The molecular structure of S8.
For an atom X, the value of the single bond covalent radius, rcov, is half of the internuclear separation in a homonuclear X-X single bond. The a- and b-forms of sulfur (orthorhombic and monoclinic sulfur, respectively) both crystallize with S8 molecules stacked in a regular arrangement; the packing in the a-form (density = 2.07 g cm-3) is more efficient than that in the b-form (density = 1.94 g cm-3).
Van der Waals forces operate between the molecules, and half of the distance of closest approach of two sulfur atoms belonging to different S8 rings is defined as the van der Waals radius, rv, of sulfur. The weakness of the bonding is evidenced by the fact that S8 vaporizes, retaining the ring structure, without absorbing much energy. The van der Waals radius of an element is necessarily larger than its covalent radius, e.g. rv and rcov for S are 185 and 103pm respectively. The van der Waals radius, rv, of an atom X is half of the distance of closest approach of two non-bonded atoms of X.
 الاكثر قراءة في نظريات التآصر الكيميائي
الاكثر قراءة في نظريات التآصر الكيميائي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















