
Language Mixture Basic examples
 المؤلف:
P. John McWhorter
المؤلف:
P. John McWhorter
 المصدر:
The Story of Human Language
المصدر:
The Story of Human Language
 الجزء والصفحة:
37-21
الجزء والصفحة:
37-21
 2024-01-17
2024-01-17
 950
950
Language Mixture Basic examples
A. Clicks in Khoi-San and Bantu. The Khoi-San (“Bushman”) languages of southern Africa are not the world’s only languages with clicks. For example, some Bantu languages spoken near them have clicks: Miriam Makeba even made the clicks famous in a popular song in her native Xhosa. These Bantu languages inherited the clicks from Khoi-San languages long ago.
B. Indo-Aryan languages. We saw that Indo-European languages in India, such as Hindi, place the verb last in a sentence.
Hindi:
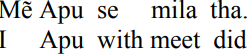
“I met Apu.”
This is not an accident. Indo-European languages of Europe usually do not place their verbs at the end of the sentence or only do so optionally. Indian Indo-European languages borrowed this word order from languages of another family originally spoken in India, the Dravidian family. Below is a sentence in one of the main Dravidian languages, Kannada:
Kannada:
Avanu nanage bisket̩annu tinisidanu.
he to-me biscuit fed
“He fed me a biscuit.”
C. Among linguists, it has always been known that languages regularly exchange words, but until rather recently, grammar mixture has often been treated as marginal, with basic processes of independent change seen as “basic.” But it is increasingly clear that all of the languages of the world bear marks from both the words and the grammars of languages spoken close by.
 الاكثر قراءة في Linguistics fields
الاكثر قراءة في Linguistics fields
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


