

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Mutations Can Affect Single Base Pairs or Longer Sequences
المؤلف:
JOCELYN E. KREBS, ELLIOTT S. GOLDSTEIN and STEPHEN T. KILPATRICK
المصدر:
LEWIN’S GENES XII
الجزء والصفحة:
27-2-2021
2268
Mutations Can Affect Single Base Pairs or Longer Sequences
KEY CONCEPTS
-A point mutation changes a single base pair.
-Point mutations can be caused by the chemical conversion of one base into another or by errors that occur during replication.
-A transition replaces a G-C base pair with an A-T base pair, or vice versa.
-A transversion replaces a purine with a pyrimidine, such as changing A-T to T-A.
-Insertions and/or deletions can result from the movement of transposable elements.
Any base pair of DNA can be mutated. A point mutation changes only a single base pair and can be caused by either of two types of event:
- Chemical modification of DNA directly changes one base into a different base.
- An error during the replication of DNA causes the wrong base to be inserted into a polynucleotide.
Point mutations can be divided into two types, depending on the nature of the base substitution:
-The most common class is the transition, which results from the substitution of one pyrimidine by the other, or of one purine by the other. This replaces a G-C pair with an A-T pair, or vice versa.
-The less common class is the transversion, in which a purine is replaced by a pyrimidine, or vice versa, so that an A-T pair becomes a T-A or C-G pair.
As shown in FIGURE 1., the mutagen nitrous acid performs an oxidative deamination that converts cytosine into uracil, resulting in a transition. In the replication cycle following the transition, the U pairs with an A, instead of the G with which the original C would have paired. So the C-G pair is replaced by a T-A pair when the A pairs with the T in the next replication cycle. (Nitrous acid can also deaminate adenine, causing the reverse transition from A-T to GC.)
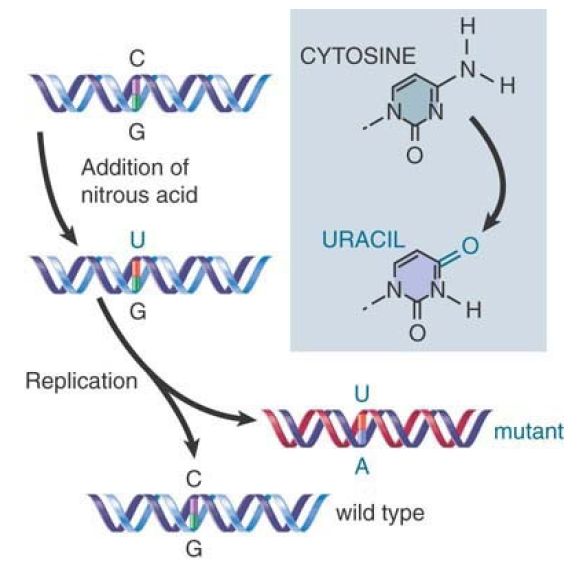
FIGURE 1. Mutations can be induced by chemical modification of a base.
Transitions are also caused by base mispairing, which occurs when noncomplementary bases pair instead of the conventional G-C and A-T base pairs. Base mispairing usually occurs as an aberration resulting from the incorporation into DNA of an abnormal base that has flexible pairing properties. FIGURE 2. shows the example of the mutagen bromouracil (BrdU), an analog of thymine that contains a bromine atom in place of thymine’s methyl group and can be
incorporated into DNA in place of thymine. BrdU has flexible pairing properties, though, because the presence of the bromine atom allows a tautomeric shift from a keto (=O) form to an enol (–OH) form. The enol form of BrdU can pair with guanine, which after replication leads to substitution of the original A-T pair by a G-C pair.
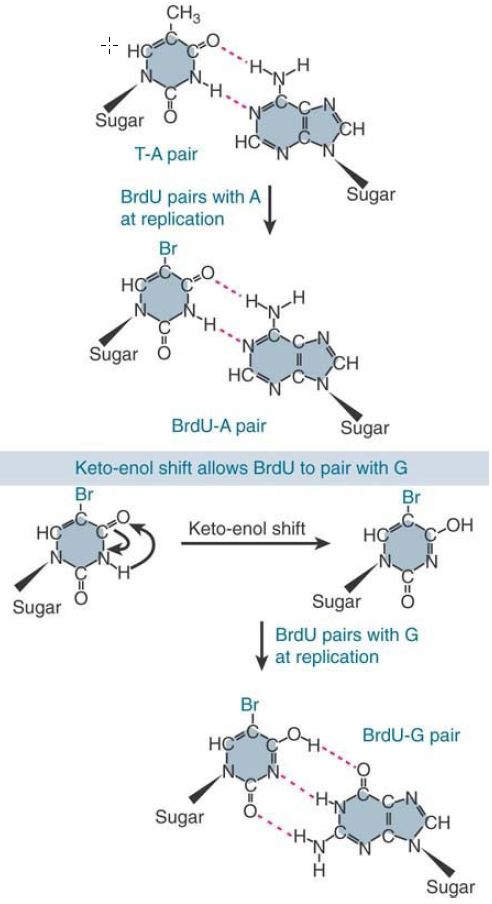
FIGURE 2. Mutations can be induced by the incorporation of base analogs into DNA.
The mistaken pairing can occur either during the original incorporation of the base or in a subsequent replication cycle. The transition is induced with a certain probability in each replication cycle, so the incorporation of BrdU has continuing effects on the sequence of DNA.
Point mutations were thought for a long time to be the principal means of change in individual genes. We now know, though, that insertions of short sequences are quite frequent. Often, the insertions are the result of transposable elements, which are sequences of DNA with the ability to move from one site to another .
An insertion within a coding region usually abolishes the activity of the gene because it can alter the reading frame; such an insertion is a frameshift mutation. (Similarly, a deletion within a coding region is usually a frameshift mutation.) Insertions of transposable elements can subsequently result in deletion of part or all of the inserted material, and sometimes of the adjacent regions.
A significant difference between point mutations and insertions is that mutagens can increase the frequency of point mutations, but do not affect the frequency of transposition. Both insertions and deletions of short sequences (often called indels) can occur by other mechanisms, however—for example, those involving errors during replication or recombination. In addition, a class of mutagens called the acridines introduces very small insertions and deletions.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















