

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Naming the Alkynes
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
18-1-2020
2361
Naming the Alkynes
Alkynes are organic molecules made of the functional group carbon-carbon triple bonds and are written in the empirical formula of CnH2n−2
. They are unsaturated hydrocarbons. Like alkenes have the suffix –ene, alkynes use the ending –yne; this suffix is used when there is only one alkyne in the molecule.

Here are the molecular formulas and names of the first ten carbon straight chain alkynes.
| Name | Molecular Formula |
|---|---|
| Ethyne | C2H2 |
| Propyne | C3H4 |
| 1-Butyne | C4H6 |
| 1-Pentyne | C5H8 |
| 1-Hexyne | C6H10 |
| 1-Heptyne | C7H12 |
| 1-Octyne | C8H14 |
| 1-Nonyne | C9H16 |
| 1-Decyne | C10H18 |
The more commonly used name for ethyne is acetylene, which used industrially.
Naming Alkynes
Like previously mentioned, the IUPAC rules are used for the naming of alkynes.
Rule 1
Find the longest carbon chain that includes both carbons of the triple bond.
Rule 2
Number the longest chain starting at the end closest to the triple bond. A 1-alkyne is referred to as a terminal alkyne and alkynes at any other position are called internal alkynes.
For example:
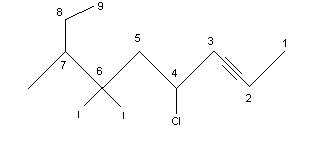.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=333&height=144)
4-chloro-6-diiodo-7-methyl-2-nonyne
Rule 3
After numbering the longest chain with the lowest number assigned to the alkyne, label each of the substituents at its corresponding carbon. While writing out the name of the molecule, arrange the substituents in alphabetical order. If there are more than one of the same substituent use the prefixes di, tri, and tetra for two, three, and four substituents respectively. These prefixes are not taken into account in the alphabetical order.
For example:
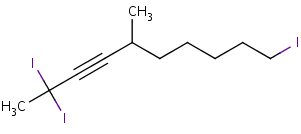
1-triiodo-4-dimethyl-2-nonyne
If there is an alcohol present in the molecule, number the longest chain starting at the end closest to it, and follow the same rules. However, the suffix would be –ynol, because the alcohol group takes priority over the triple bond.
.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=322&height=126)
5- methyl-7-octyn-3-ol
When there are two triple bonds in the molecule, find the longest carbon chain including both the triple bonds. Number the longest chain starting at the end closest to the triple bond that appears first. The suffix that would be used to name this molecule would be –diyne.
For example:
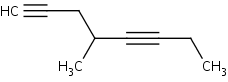
4-methyl-1,5-octadiyne
Rule 4
Substituents containing a triple bond are called alkynyl.
For example:
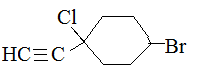.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=210&height=80)
1-chloro-1-ethynyl-4-bromocyclohexane
Here is a table with a few of the alkynyl substituents:
| Name | Molecule |
|---|---|
| Ethynyl | -C≡CH |
| 2- Propynyl | -CH2C≡CH |
| 2-Butynyl | -CH3C≡CH2CH3 |
Rule 5
A molecule that contains both double and triple bonds is called an alkenyne. The chain can be numbered starting with the end closest to the functional group that appears first. For example:
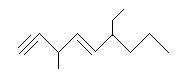.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=191&height=81)
6-ethyl-3-methyl-1,4-nonenyne
 الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















