

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Features of a C-13 NMR spectrum
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
6-1-2020
1812
Features of a C-13 NMR spectrum
Butane shows two different peaks in the 13C NMR spectrum, below. Note that: the chemical shifts of these peaks are not very different from methane. The carbons in butane are in a similar environment to the one in methane.
- there are two distinct carbons in butane: the methyl, or CH3, carbon, and the methylene, or CH2, carbon.
- the methyl carbon absorbs slightly upfield, or at lower shift, around 10 ppm.
- the methylene carbon absorbs at slightly downfield, or at higher shift, around 20 ppm.
- other factors being equal, methylene carbons show up at slightly higher shift than methyl carbons.
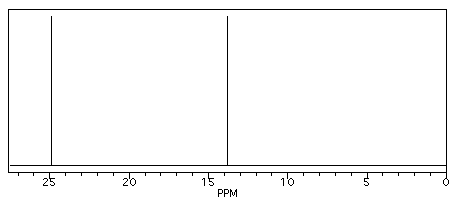
Figure NMR2. Simulated 13C NMR spectrum of butane (showing only the upfield portion of the spectrum).
In the 13C NMR spectrum of pentane (below), you can see three different peaks, even though pentane just contains methyl carbons and methylene carbons like butane. As far as the NMR spectrometer is concerned, pentane contains three different kinds of carbon, in three different environments. That result comes from symmetry.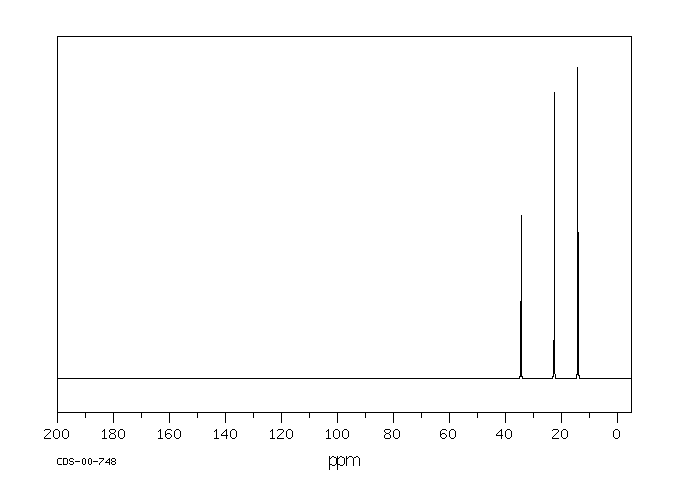
Figure NMR3.13C NMR spectrum of pentane. Source: SDBSWeb : http://riodb01.ibase.aist.go.jp/sdbs/ (National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology of Japan, 15 August 2008)
Symmetry is an important factor in spectroscopy. Nature says:
- atoms that are symmetry-inequivalent can absorb at different shifts.
- atoms that are symmetry-equivalent must absorb at the same shift.
To learn about symmetry, take a model of pentane and do the following:
- make sure the model is twisted into the most symmetric shape possible: a nice "W".
- choose one of the methyl carbons to focus on.
- rotate the model 180 degrees so that you are looking at the same "W" but from the other side.
- note that the methyl you were focusing on has simply switched places with the other methyl group. These two carbons are symmetry-equivalent via two-fold rotation.
Animation NMR1. A three-dimensional model of pentane. Grab the model with the mouse and rotate it so that you are convinced that the second and fourth carbons are symmetry-equivalent, but the third carbon is not.
By the same process, you can see that the second and fourth carbons along the chain are also symmetry-equivalent. However, the middle carbon is not; it never switches places with the other carbons if you rotate the model. There are three different sets of inequivalent carbons; these three groups are not the same as each other according to symmetry.
 الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















