

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Structure Determination in Conjugated Systems: Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
18-8-2019
1891
Ultraviolet spectroscopy provides much less information about the structure of molecules than do the spectroscopic techniques studied earlier (infrared spectroscopy, mass spectroscopy, and NMR spectroscopy). Thus, your study of this technique will be restricted to a brief overview. You should, however, note that for an organic chemist, the most useful ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum is that in which the radiation has a wavelength of between 200 and 400 nm.
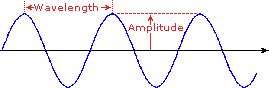
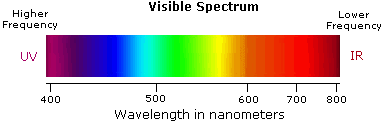
- Violet: 400 - 420 nm
- Indigo: 420 - 440 nm
- Blue: 440 - 490 nm
- Green: 490 - 570 nm
- Yellow: 570 - 585 nm
- Orange: 585 - 620 nm
- Red: 620 - 780 nm
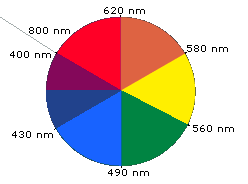
When white light passes through or is reflected by a colored substance, a characteristic portion of the mixed wavelengths is absorbed. The remaining light will then assume the complementary color to the wavelength(s) absorbed. This relationship is demonstrated by the color wheel shown below. Here, complementary colors are diametrically opposite each other. Thus, absorption of 420-430 nm light renders a substance yellow, and absorption of 500-520 nm light makes it red. Green is unique in that it can be created by absoption close to 400 nm as well as absorption near 800 nm.
Early humans valued colored pigments, and used them for decorative purposes. Many of these were inorganic minerals, but several important organic dyes were also known. These included the crimson pigment, kermesic acid, the blue dye, indigo, and the yellow saffron pigment, crocetin. A rare dibromo-indigo derivative, punicin, was used to color the robes of the royal and wealthy. The deep orange hydrocarbon carotene is widely distributed in plants, but is not sufficiently stable to be used as permanent pigment, other than for food coloring. A common feature of all these colored compounds, displayed below, is a system of extensively conjugated π-electrons.
 الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















