

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Racemic Mixtures and the Resolution of Enantiomers
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
7-7-2019
1996
As noted earlier, chiral compounds synthesized from achiral starting materials and reagents are generally racemic (i.e. a 50:50 mixture of enantiomers). Separation of racemates into their component enantiomers is a process called resolution. Since enantiomers have identical physical properties, such as solubility and melting point, resolution is extremely difficult. Diastereomers, on the other hand, have different physical properties, and this fact is used to achieve resolution of racemates. Reaction of a racemate with an enantiomerically pure chiral reagent gives a mixture of diastereomers, which can be separated. For example, if a racemic mixture of a chiral alcohol is reacted with a enantiomerically pure carboxylic acid, the result is a mixture of diastereomers: in this case, because the pure (R) entantiomer of the acid was used, the product is a mixture of (R-R) and (R-S) diastereomeric esters, which can, in theory, be separated by their different physical properties. Subsequent hydrolysis of each separated ester will yield the 'resolved' (enantiomerically pure) alcohols. The used in this technique are known as 'Moscher's esters', after Harry Stone Moscher, a chemist who pioneered the method at Stanford University.
As noted earlier, chiral compounds synthesized from achiral starting materials and reagents are generally racemic (i.e. a 50:50 mixture of enantiomers). Separation of racemates into their component enantiomers is a process called resolution. Since enantiomers have identical physical properties, such as solubility and melting point, resolution is extremely difficult. Diastereomers, on the other hand, have different physical properties, and this fact is used to achieve resolution of racemates. Reaction of a racemate with an enantiomerically pure chiral reagent gives a mixture of diastereomers, which can be separated. Reversing the first reaction then leads to the separated enantiomers plus the recovered reagent.
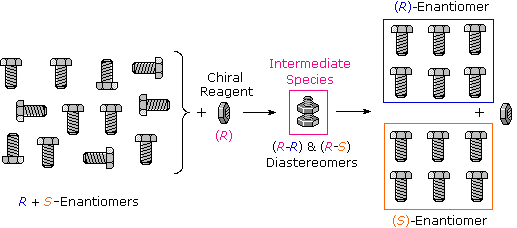
Figure 1.1: Many kinds of chemical and physical reactions, including salt formation, may be used to achieve the diastereomeric intermediates needed for separation.
Figure 1.1 illustrates this general principle by showing how a nut having a right-handed thread (R) could serve as a "reagent" to discriminate and separate a mixture of right- and left-handed bolts of identical size and weight. Only the two right-handed partners can interact to give a fully-threaded intermediate, so separation is fairly simple. The resolving moiety, i.e. the nut, is then removed, leaving the bolts separated into their right and left-handed forms. Chemical reactions of enantiomers are normally not so dramatically different, but a practical distinction is nevertheless possible.
Because the physical properties of enantiomers are identical, they seldom can be separated by simple physical methods, such as fractional crystallization or distillation. It is only under the influence of another chiral substance that enantiomers behave differently, and almost all methods of resolution of enantiomers are based upon this fact. We include here a discussion of the primary methods of resolution
 الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















