
Nucleophilic Addition Reactions & Reduction of alkynes
 المؤلف:
William Reusch
المؤلف:
William Reusch
 المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
............
الجزء والصفحة:
............
 8-10-2018
8-10-2018
 3096
3096
Nucleophilic Addition Reactions & Reduction of alkynes
The sp-hybrid carbon atoms of the triple-bond render alkynes more electrophilic than similarly substituted alkenes. As a result, alkynes sometimes undergo addition reactions initiated by bonding to a nucleophile. This mode of reaction, illustrated below, is generally not displayed by alkenes, unless the double-bond is activated by electronegative substituents, e.g. F2C=CF2, or by conjugation with an electron withdrawing group.
HC≡CH + KOC2H5 in C2H5OH at 150 ºC ——> H2C=CH-OC2H5
HC≡CH + HCN + NaCN (catalytic) ——> H2C=CH-CN
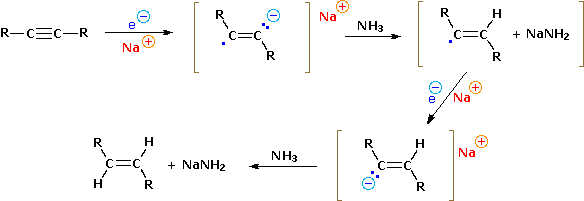
The smallest and most reactive nucleophilic species is probably an electron. Electron addition to a functional group is by definition a reduction, and we noted earlier that alkynes are reduced by solutions of sodium in liquid ammonia to trans-alkenes. To understand how this reduction occurs we first need to identify two distinct reactions of sodium with liquid ammonia (boiling point -78 ºC). In the first, sodium dissolves in the pure liquid to give a deep blue solution consisting of very mobile and loosely bound electrons together with solvated sodium cations (first equation below). For practical purposes, we can consider such solutions to be a source of "free electrons" which may be used as powerful reducing agents. In the second case, ferric salts catalyze the reaction of sodium with ammonia, liberating hydrogen and forming the colorless salt sodium amide (second equation). This is analogous to the reaction of sodium with water to give sodium hydroxide, but since ammonia is 1018 times weaker an acid than water, the reaction is less violent. The usefulness of this reaction is that sodium amide, NaNH2, is an exceedingly strong base (18 powers of ten stronger than sodium hydroxide), which may be used to convert very weak acids into their conjugate bases.
| Na + NH3 (liquid, –78 ºC ) ——> Na(+) + e(–) (a blue solution) |
| Na + NH3 (liquid, –78 ºC ) + Fe ——> H2 + NaNH2 (a colorless solution) |
Returning to the reducing capability of the blue electron solutions, we can write a plausible mechanism for the reduction of alkynes to trans-alkenes, as shown below. Isolated carbon double-bonds are not reduced by sodium in liquid ammonia, confirming the electronegativity difference between sp and sp2 hybridized carbons.
 الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
الاكثر قراءة في الهايدروكاربونات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


