
RATE LAWS
 المؤلف:
Arun Bahl, B.S. Bahl and G.D.Tuli
المؤلف:
Arun Bahl, B.S. Bahl and G.D.Tuli
 المصدر:
Essential Physical Chemistry
المصدر:
Essential Physical Chemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 734
الجزء والصفحة:
p 734
 22-9-2018
22-9-2018
 661
661
RATE LAWS
At a fixed temperature the rate of a given reaction depends on concentration of reactants.
The exact relation between concentration and rate is determined by measuring the reaction rate with different initial reactant concentrations. By a study of numerous reactions it is shown that : the rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the reactant concentrations, each concentration being raised to some power.
Thus for a substance A undergoing reaction,
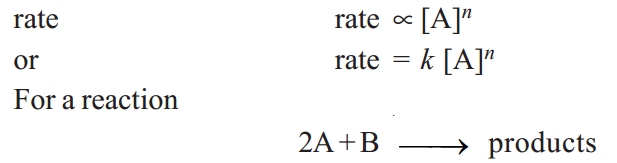 …..(1)
…..(1)
the reaction rate with respect to Aor Bis determined by varying the concentration of one reactant, keeping that of the other constant. Thus the rate of reaction may be expressed as
rate = k [A]m[B]n ……….…..(2)
Expressions such as (1) and (2) tell the relation between the rate of a reaction and reactant concentrations.
An expression which shows how the reaction rate is related to concentrations is called the rate law or rate equation.
The power (exponent) of concentration nor min the rate law is usually a small whole number integer (1, 2, 3) or fractional. The proportionality constant kis called the rate constantfor the reaction.
Examples of rate law :
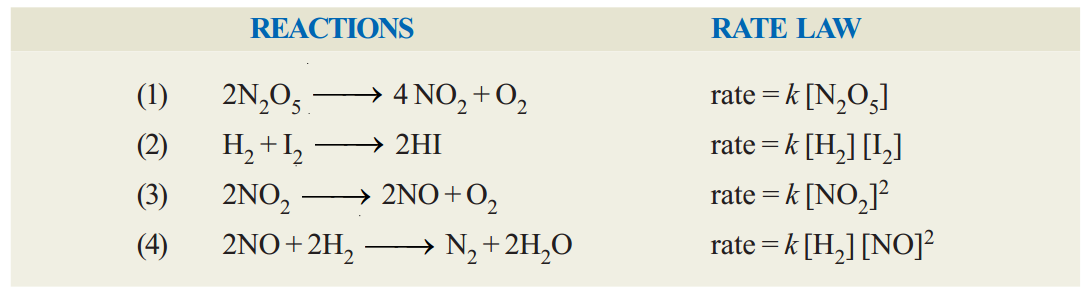
In these rate laws where the quotient or concentration is not shown, it is understood to be 1. That is [H2]1= [H2].
It is apparent that the rate law for a reaction must be determined by experiment. It cannot be written by merely looking at the equation with a background of our knowledge of Law of Mass Action.
However, for some elementary reactions the powers in the rate law may correspond to coefficients in the chemical equation. But usually the powers of concentration in the rate law are different from coefficients. Thus for the reaction (4) above, the rate is found to be proportional to [H2] although thequotient of H2 in the equation is 2. For NO the rate is proportional to [NO]2 and power ‘2’ corresponds to the coefficient.
 الاكثر قراءة في حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية
الاكثر قراءة في حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


