

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Mass Spectrum for Isotopes
المؤلف:
William Reusch
المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
............
10-8-2018
2557
Isotopes
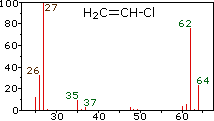
Since a mass spectrometer separates and detects ions of slightly different masses, it easily distinguishes different isotopes of a given element. This is manifested most dramatically for compounds containing bromine and chlorine, as illustrated by the following examples. Since molecules of bromine have only two atoms, the spectrum on the left will come as a surprise if a single atomic mass of 80 amu is assumed for Br. The five peaks in this spectrum demonstrate clearly that natural bromine consists of a nearly 50:50 mixture of isotopes having atomic masses of 79 and 81 amu respectively. Thus, the bromine molecule may be composed of two 79Br atoms (mass 158 amu), two 81Br atoms (mass 162 amu) or the more probable combination of 79Br-81Br (mass 160 amu). Fragmentation of Br2 to a bromine cation then gives rise to equal sized ion peaks at 79 and 81 amu.
 |
 |
 |
||
|
bromine |
vinyl chloride |
methylene chloride |
|---|
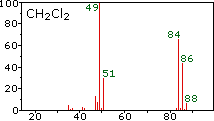
The center and right hand spectra show that chlorine is also composed of two isotopes, the more abundant having a mass of 35 amu, and the minor isotope a mass 37 amu. The precise isotopic composition of chlorine and bromine is:
Chlorine: 75.77% 35Cl and 24.23% 37Cl
Bromine: 50.50% 79Br and 49.50% 81Br
The presence of chlorine or bromine in a molecule or ion is easily detected by noticing the intensity ratios of ions differing by 2 amu. In the case of methylene chloride, the molecular ion consists of three peaks at m/z=84, 86 & 88 amu, and their diminishing intensities may be calculated from the natural abundances given above. Loss of a chlorine atom gives two isotopic fragment ions at m/z=49 & 51amu, clearly incorporating a single chlorine atom. Fluorine and iodine, by contrast, are monoisotopic, having masses of 19 amu and 127 amu respectively. It should be noted that the presence of halogen atoms in a molecule or fragment ion does not change the odd-even mass rules given above.
 الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















