

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Acid-base extraction
المؤلف:
Chris Schaller-Professor (Chemistry)
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
............
23-7-2018
3686
Acid-base extraction
An acid-base extraction is a type of liquid-liquid extraction. It typically involves different solubility levels in water and an organic solvent. The organic solvent may be any carbon-based liqiuid that does not dissolve very well in water; common ones are ether, ethyl acetate, or dichloromethane.
Acid-base extraction is typically used to separate organic compounds from each other based on their acid-base properties. The method rests on the assumption that most organic compounds are more soluble in organic solvents than they are in water. However, if the organic compound is rendered ionic, it becomes more soluble in water than in the organic solvent. These compounds can easily be made into ions either by adding a proton (an H+ ion), making the compound into a positive ion, or by removing a proton, making the compound into a negative ion.
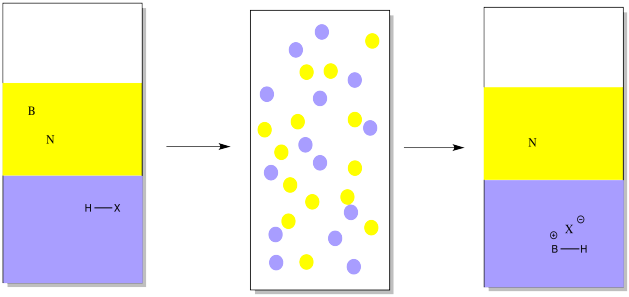
Suppose you have a mixture of two compounds. There is a neutral one which doesn't react with any acids or bases. There is also a basic one, which reacts with acids by picking up a proton. In this case, a proton might be added via reaction with a strong mineral acid (represented by HX in the drawing). Suppose an aqueous solution of mineral acid, such as HCl, were shaken vigorously with an ethereal solution of an organic base and an organic neutral. The proton would be transferred to a basic compound, but not to a neutral one. The basic compound would become ionic, and more water-soluble.
Note that in the drawing, the ether is represented in yellow, whereas the water is shown in blue. The water is on the bottom in this case because water has a higher density than ether, so it will sink to the bottom (along with anything dissolved in it). Some organic solvents do have a higher density than water, so the aqueous solution would float to the top in those case.
As a result, the ethereal solution would contain only the neutral compound, not the basic one. The neutral compound could be isolated simply by evaporating the ether.
However, as a practical matter, the ether would have to be dried first. What's the difference between evaporating and drying? Have you ever been to the beach or taken a shower? Drying refers to the removal of water. This step is necessary because ether tends to dissolve a lot of water in it. Once the ether has been evaporated, there would be some neutral compound, but it would be mixed with water.
Water removal is most easily done by adding a drying agent, such as magnesium sulfate or sodium sulfate. The water sticks to these solids, which are then filtered off.
Now the neutral compound is alone in the ether. Evaporation of the ether gives the pure, neutral compound.
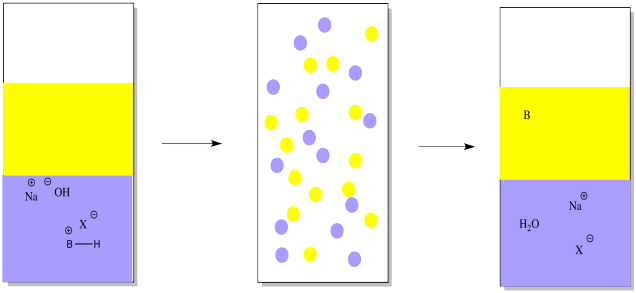
However, the basic compound is stuck in the water, and it isn't the same compound anymore. It's an ion, now. If we want the original compound in a pure form, we need to take that proton away. That can be done by adding a mineral base, such as sodium hydroxide.
The mineral base will remove the proton, leaving the original organic compound. The organic compound is uncharged and not as soluble in water anymore. It will go back into the ether layer.
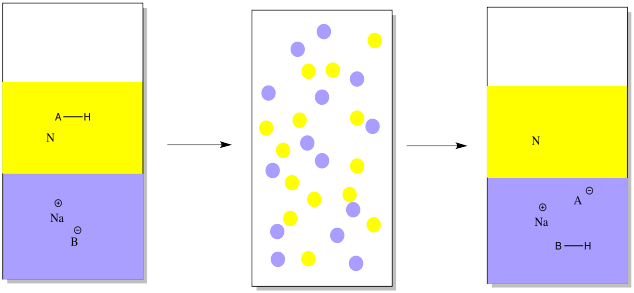
Conversely, we might have a mixture of an acidic organic compound and a neutral compound to start out with. In that case, we would add a mineral base in the first place, to take a proton away from the acidic compound. The mineral base might be something like sodium hydroxide or sodium bicarbonate. In the drawing, it is just represented as Na+ B-.
The acidic compound becomes ionic and water-soluble when it loses a proton. That leaves the neutral compound alone.
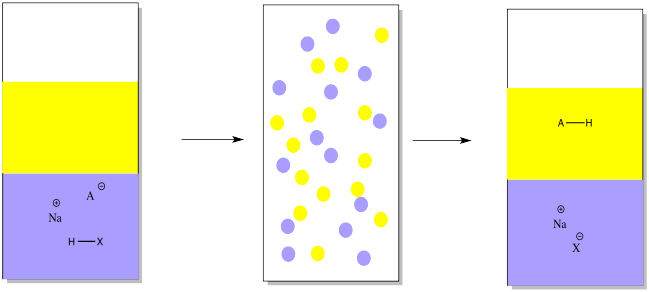
To get that acidic compound back, we would add a mineral acid such as hydrochloric acid in order to restore the missing proton.
Just as in the other case, the ether layer containing a pure compound could be separated, dried and evaporated in order to provide the pure compound.
 الاكثر قراءة في طرق الفصل والتنقية
الاكثر قراءة في طرق الفصل والتنقية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















