
Polysaccharides
 المؤلف:
William Reusch
المؤلف:
William Reusch
 المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
............
الجزء والصفحة:
............
 20-7-2018
20-7-2018
 3743
3743
Polysaccharides
As the name implies, polysaccharides are large high-molecular weight molecules constructed by joining monosaccharide units together by glycosidic bonds. They are sometimes called glycans. The most important compounds in this class, cellulose, starch and glycogen are all polymers of glucose. This is easily demonstrated by acid-catalyzed hydrolysis to the monosaccharide. Since partial hydrolysis of cellulose gives varying amounts of cellobiose, we conclude the glucose units in this macromolecule are joined by beta-glycoside bonds between C-1 and C-4 sites of adjacent sugars. Partial hydrolysis of starch and glycogen produces the disaccharide maltose together with low molecular weight dextrans, polysaccharides in which glucose molecules are joined by alpha-glycoside links between C-1 and C-6, as well as the alpha C-1 to C-4 links found in maltose. Polysaccharides built from other monosaccharides (e.g. mannose, galactose, xylose and arabinose) are also known, but will not be discussed here.
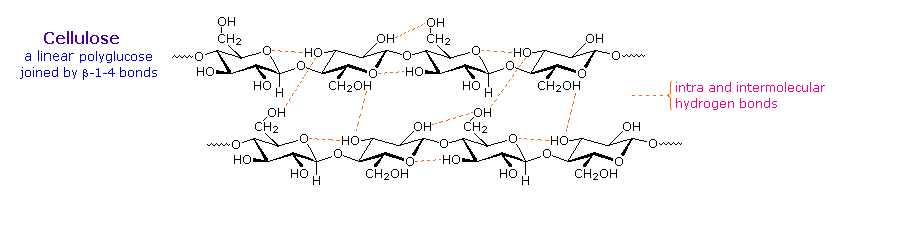
Over half of the total organic carbon in the earth's biosphere is in cellulose. Cotton fibers are essentially pure cellulose, and the wood of bushes and trees is about 50% cellulose. As a polymer of glucose, cellulose has the formula (C6H10O5)n where n ranges from 500 to 5,000, depending on the source of the polymer. The glucose units in cellulose are linked in a linear fashion, as shown in the drawing below. The beta-glycoside bonds permit these chains to stretch out, and this conformation is stabilized by intramolecular hydrogen bonds. A parallel orientation of adjacent chains is also favored by intermolecular hydrogen bonds. Although an individual hydrogen bond is relatively weak, many such bonds acting together can impart great stability to certain conformations of large molecules. Most animals cannot digest cellulose as a food, and in the diets of humans this part of our vegetable intake functions as roughage and is eliminated largely unchanged. Some animals (the cow and termites, for example) harbor intestinal microorganisms that breakdown cellulose into monosaccharide nutrients by the use of beta-glycosidase enzymes.
Cellulose is commonly accompanied by a lower molecular weight, branched, amorphous polymer called hemicellulose. In contrast to cellulose, hemicellulose is structurally weak and is easily hydrolyzed by dilute acid or base. Also, many enzymes catalyze its hydrolysis. Hemicelluloses are composed of many D-pentose sugars, with xylose being the major component. Mannose and mannuronic acid are often present, as well as galactose and galacturonic acid.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكاربوهيدرات
الاكثر قراءة في الكاربوهيدرات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


