


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 17-6-2019
Date: 25-7-2020
Date: 26-2-2019
|
Activated charcoal: utilizing a porous structure
Activated charcoal is a finely divided form of amorphous carbon and is manufactured from organic materials (e.g. peat, wood) by heating in the presence of reagents that promote both oxidation and dehydration. Activated charcoal possesses a pore structure with a large internal surface area: microporous materials exhibit pores < 2nm wide, macroporous refers to activated charcoals with a pore size >50 nm, and mesoporous materials fall in between these extremes. The largest internal surface areas are found for microporous materials (>700m2 g-1). The ability of the hydrophobic surface to adsorb small molecules is the key to the widespread applications of activated charcoal.
Early large-scale applications of activated charcoal were in gas masks in World War I. Various gas-filters including those in cooker extractors and mobile or bench-top laboratory fume-hoods contain activated charcoal filters. About 20% of the activated charcoal that is produced is consumed in the sugar industry, where it is used as a decolouring agent.
Water purification uses large amounts of activated charcoal. The porous structure means that activated charcoal is an excellent heterogeneous catalyst, especially when impregnated with a d-block metal such as palladium. On an industrial scale, it is used, for example, in the manufacture of phosgene (equation 13.42), and in laboratory syntheses, it has many uses, e.g.:
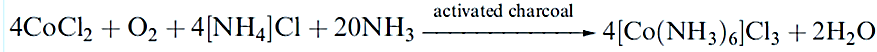
The porous skeleton of activated carbon can be used as a template on which to construct other porous materials, for example, SiO2, TiO2 and Al2O3. The oxide is first dissolved in supercritical CO2 and then the activated carbon template is coated in the supercritical fluid. The carbon template is removed by treatment with oxygen plasma or by calcination in air at 870 K, leaving a nanoporous (‘nano’ refers to the scale of the pore size) metal oxide with a macroporous structure that mimics that of the activated carbon template.



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جمعية العميد تدعو الجامعات العراقية لحضور مؤتمرها العلمي السابع
|
|
|