

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
β1-ADRENERGIC ANTAGONISTS ‘ β-BLOCKERS’
المؤلف:
James R Hanson
المصدر:
Chemistry and Medicines
الجزء والصفحة:
p 59
9-10-2017
1420
β1-ADRENERGIC ANTAGONISTS ‘ β-BLOCKERS’
Patients with angina suffer severe chest pain on exercise. Exercise requires the heart to work harder and supply more blood. In order to do this the heart requires more oxygen and nutrients from the blood that is supplying the heart muscle. If the arteries supplying the heart are blocked, there are problems of blood supply. The heart has to work harder to fulfil the need and this overwork eventually produces a heart attack. The cardiac activity producing an increase in heart rate is stimulated by catecholamines acting at the β1-receptors. A drug, which was an antagonist, a β-blocker, should prevent the heart rate rising by blocking the effect of sympathetic nerve stimulation. The heart’s demand for oxygen should then be reduced.
One of the first compounds to show this effect was a partial agonist, dichloroisoprenaline 3.49, which was prepared in 1958. However, this also had effects on bronchial muscle. In 1961 replacement of the two chlorines by a further aromatic ring gave the naphthalene derivative, pronethalol 3.50. This compound was a potent β-blocker but unfortunately it produced thymic tumours in mice and in 1963 it had to be withdrawn from trials. Propranolol 3.51 prepared from α-naphthol proved to be a successful substitute. Interestingly, the analogue made from β-naphthol and which at first sight appears to be more closely related to pronethalol, was less active. The side chain alcohol is chiral.
Structure:activity studies showed that the activity resided in the R series and that the compounds required a free N–H. Propranolol 3.51 is synthesized from α-naphthol and l-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane followed by cleavage of the epoxide. There has been considerable interest in preparing a chiral version of the drug.
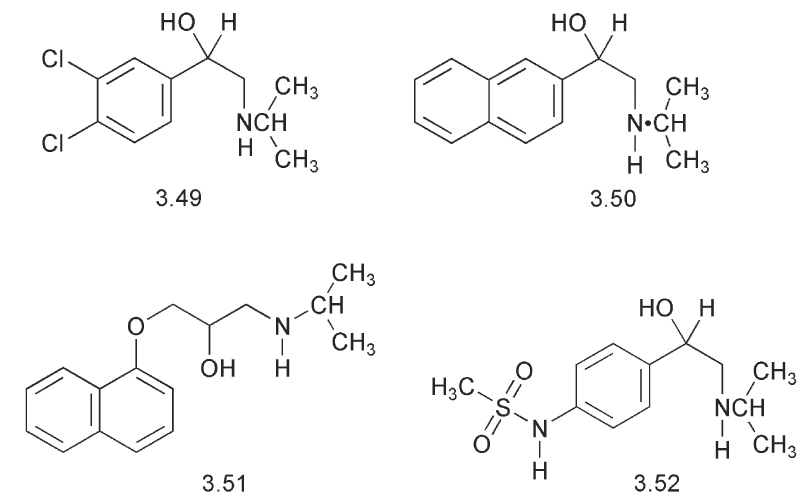
Propranolol 3.51 is a lipophilic compound and hence it has a high octanol:water partition coefficient. This high lipophilicity is known to facilitate the transfer of compounds across the blood:brain barrier and this could be the reason for some of the side effects associated with the action of propranolol on the CNS. Hence a number of less hydrophobic compounds were synthesized. Sotalol 3.52, in which the sulfonamide mimics the acidity of a phenol, showed some β-receptor-binding properties.
Practolol 3.53, synthesized from paracetamol, has a log P of 0.71 (corresponding to a partition coefficient of 6:1 between octanol and water) while propranolol 3.51 has a log P of 3.65 corresponding to a partition coefficient of 4500:1. Because it did not cross the blood:brain barrier as easily as propanol, this compound had fewer CNS side effects and was more cardioselective. However, toxicity developed in some patients. This led to the development of atenolol 3.54, which did not suffer from these problems.

 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















