

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
DRUG METABOLISM
المؤلف:
James R Hanson
المصدر:
Chemistry and Medicines
الجزء والصفحة:
P25
18-1-2016
2038
DRUG METABOLISM
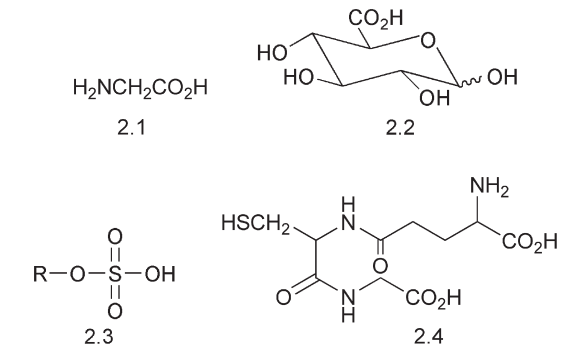
A drug may undergo a metabolic change at any stage after ingestion, both prior to reaching its site of action and afterwards. Much of drug metabolism takes place in the intestine and in the liver. The metabolic changes may lead to the deactivation and excretion of a compound before it has had any effect, bringing about the first pass loss. The metabolism of a drug may also change its activity and bring about side effects. In other instances the metabolite may actually be the active species. In these cases there is a pro-drug:drug relationship. As the drug passess through the system it is exposed to the digestive enzymes, which are often hydrolytic in their action. The bacterial action in the intestine is often reductive while the metabolism in the liver is often oxidative in character. It is possible to distinguish two phases in the metabolism of a drug. In phase one, changes are brought about to the drug itself. Alcohols and aldehydes may be oxidized, hydroxyl or epoxide groups may be inserted, alkyl groups may be removed from nitrogen or oxygen and polar functional groups such as amino and hydroxyl groups unmasked by the hydrolysis of amides and esters. In phase two, a polar molecule such as glycine 2.1, the sugar derivative, glucuronic acid 2.2, a sulfate group 2.3 or the tripeptide glutathione 2.4 is linked to the drug by a process known as ‘conjugation’. The overall effect of these changes is to increase the water solubility of the drug and to diminish its lipid solubility. This in turn can diminish the likelihood of it crossing various barriers and reaching its site of action. The addition of glutathione may remove a toxic metabolite.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















