

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
MUSCARINIC AGONISTS
المؤلف:
James R Hanson
المصدر:
Chemistry and Medicines
الجزء والصفحة:
p 51
8-10-2017
1810
MUSCARINIC AGONISTS
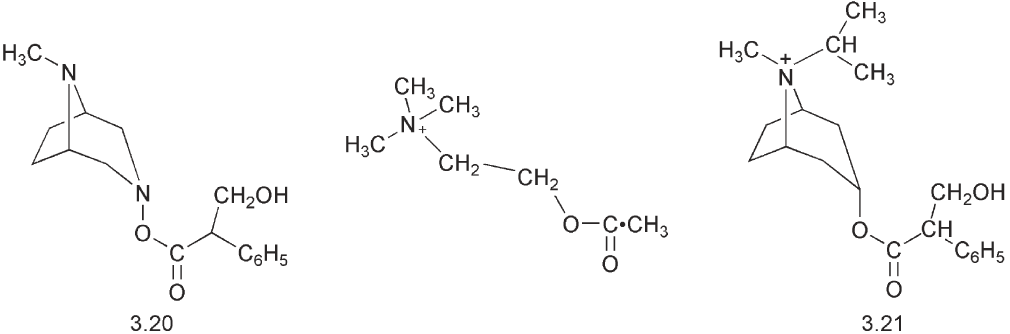
Muscarinic agonists are used in ophthalmology in the treatment of glaucoma. The alkaloid atropine 3.20 was obtained from the plant, deadly nightshade, Atropa belladonna, which was used in the Middle Ages both because of its properties in dilating the pupils of the eye supposedly to make women more glamorous and also because of its poisonous effects. Atropine is a muscarinic antagonist. It binds competitively and prevents acetylcholine from functioning. It dilates the pupil of the eye and hence it is used in ophthalmology. Atropine is relatively lipophilic and as the free amine, it can cross the blood:brain barrier and produce effects on the CNS. However, quaternary salts of atropine such as ipratropium bromide 3.21 do not cross the blood:brain barrier and are used as muscarinic antagonists in bronchial dilation and muscle relaxation.
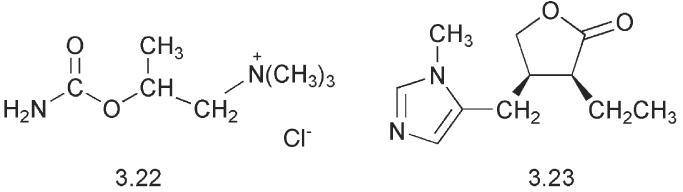
Cholinergic agonists have some other medicinal applications. Bethanechol 3.22 is a carbamate rather than an ester and therefore it is not easily hydrolysed by acetylcholine esterase increasing its persistence. It stimulates muscarinic receptors and it is used to facilitate urinary expulsion. The alkaloid pilocarpine 3.23 is a g-lactone and is also stable to acetylcholinesterase. It exhibits muscarinic activity and it is used in ophthalmology to stimulate secretion from the eye and hence reduce intraocular pressure in glaucoma. It is helpful to see a similarity in this structure both to acetylcholine and to muscarine.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















