


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 30-8-2016
Date: 14-8-2016
Date: 30-8-2016
|
Gas Fluctuations
A high-vacuum chamber is evacuated to a pressure of 10-11 atm. Inside the chamber there is a thin-walled ballast volume filled with helium gas at a pressure P = 10-6 atm and a temperature T = 293 K. On one wall of this ballast volume, there is a small hole of area A = 10-3 cm2. A detector counts the number of particles leaving the ballast volume during time intervals ∆t = 1 ms.
a) Find the average number of molecules counted by the detector.
b) Find the mean square fluctuation of this number.
c) What is the probability of not counting any particles in one of the measurements?
SOLUTION
a) We can disregard any particles from the high-vacuum part of the setup and consider the problem of molecular flow from the ballast volume into the vacuum chamber. The number of particles was calculated
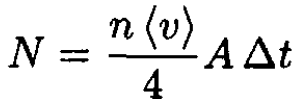 (1)
(1)
where n is the particle concentration and ⟨v⟩ is the average velocity. Expressing n via the pressure P and using
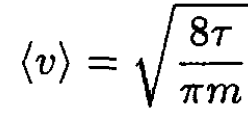 (2)
(2)
we obtain
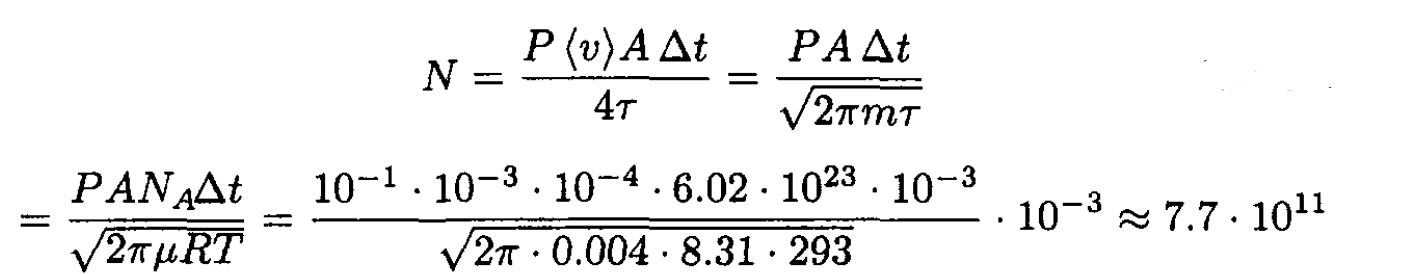 (3)
(3)
b) At the given pressure the molecules are in the Knudsen regime, the mean free path λ >> A1/2. Therefore, we can assume that the molecular distribution will not change and N can be obtained from the Poisson distribution. The mean fluctuation
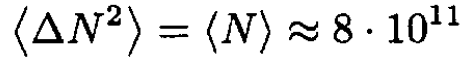 (4)
(4)
The mean relative fluctuation is given by
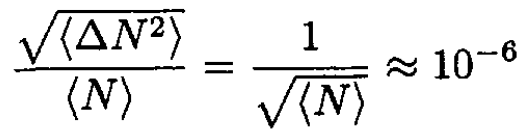 (5)
(5)
c) The probability of finding N particles as a result of one of the measurements, according to the Poisson distribution, is
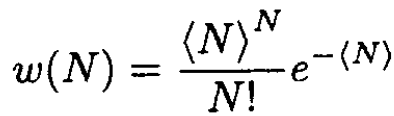 (6)
(6)
Therefore, the probability of counting zero particles in 1 ms is
 (7)
(7)
an exceedingly small number.



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تستعد لإطلاق الحفل المركزي لتخرج طلبة الجامعات العراقية
|
|
|