


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 21-2-2016
Date: 2025-02-13
Date: 21-2-2016
|
Definition
• An autoimmune disorder caused by an abnormal immune response to dietary gluten.
Epidemiology
• Common, affecting ~1% of the population.
Aetiology
• Dietary gluten and related proteins.
Pathogenesis
• the culprit proteins are poorly digested by intestinal proteases.
• Intact peptides enter the lamina propria and are deamidated by tissue transglutaminase, rendering them negatively charged.
• Negatively charged peptides bind more efficiently to human leucocyte antigen (HLA) receptors on antigen- presenting cells which are recognized by intestinal T- cells.
• Activated T- cells stimulate an immune reaction in the intestinal wall.
Presentation
• Symptoms relating to the GI tract may be present such as weight loss, abdominal pain, and diarrhoea.
• however, many patients are asymptomatic and only diagnosed during investigation of an iron deficiency anaemia.
Serology
• Presence of serum IgA endomysial or transglutaminase antibodies is highly specific and sensitive for coeliac disease. Care must be taken in interpreting these results in patients who are IgA- deficient.
Macroscopy
• Blunting and flattening of villi may be visible under a dissecting microscope (and may be identified at endoscopy).
Histopathology
• fully developed cases show increased intraepithelial lymphocytes (>20/ 100 epithelial cells), mainly at the tips of the villi, many lymphocytes and plasma cells in the lamina propria, villous atrophy, and crypt hyperplasia (fig. 1).
• Milder cases may only show increased intraepithelial lymphocytes without villous atrophy. this is termed lymphocytic duodenitis.
* Note that none of these changes are specific to coeliac disease; identical changes can be seen in a number of other conditions, e.g. drugs, tropical sprue. Biopsy findings must be interpreted in light of the clinical and serological picture.
Prognosis
• Strict adherence to a gluten- free diet leads to resolution of symptoms and normalization of histology, although architectural changes may take some time to normalize. Cases which do not respond to a gluten- free diet need to be carefully assessed for the development of a lymphoma.
• Increased risk of type 1 diabetes, autoimmune thyroid disease, dermatitis herpetiformis, oropharyngeal and oesophageal carcinomas, small bowel adenocarcinoma, and a rare, but highly aggressive, form of t- cell lymphoma known as enteropathy- associated t- cell lymphoma (EATL).
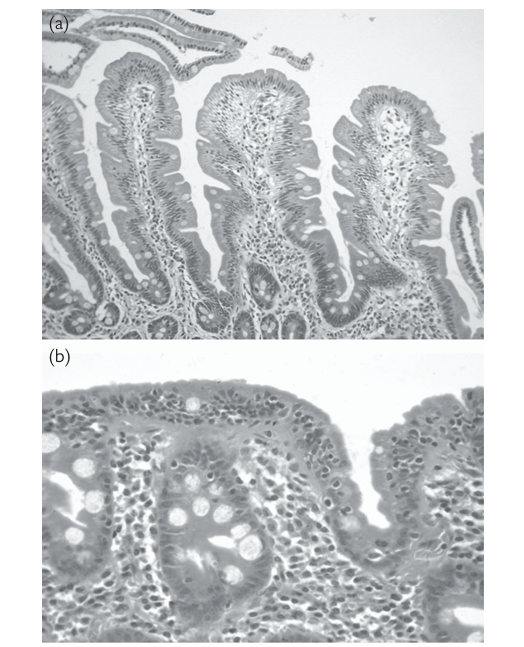
FIG1. (a) Normal duodenal mucosa. the villi have a normal height and shape, and there is no increase in intraepithelial lymphocytes. (b) Duodenal biopsy from a patient with gluten- sensitive enteropathy. the villi have completely disappeared and the surface epithelium contains many intraepithelial lymphocytes . reproduced with permission from Clinical Pathology (Oxford Core texts), Carton, James, Daly, richard, and ramani, Pramila, Oxford University Press (2006), p.154, figure 8.8.



|
|
|
|
للعاملين في الليل.. حيلة صحية تجنبكم خطر هذا النوع من العمل
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"ناسا" تحتفي برائد الفضاء السوفياتي يوري غاغارين
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|