


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 3-3-2016
Date: 2-3-2016
Date: 6-3-2016
|
Many bacteria synthesize large amounts of extracellular polymer when growing in their natural environments. With one known exception (the poly-d-glutamic acid capsules of Bacillus anthracis and Bacillus licheniformis), the extracellular material is polysaccharide (Table 1). The terms capsule and slime layer are frequently used to describe polysaccharide layers; the more inclusive term glycocalyx is also used. Glycocalyx is defined as the polysaccharide-containing mate rial lying outside the cell. A condensed, well-defined layer closely surrounding the cell that excludes particles, such as India ink, is referred to as a capsule (Figure 1). If the glycocalyx is loosely associated with the cell and does not exclude particles, it is referred to as a slime layer. Extracellular polymer is synthesized by enzymes located at the surface of the bacterial cell. Streptococcus mutans, for example, uses two enzymes—glucosyl transferase and fructosyl transferase—to synthesize long-chain dextrans (poly-d-glucose) and levans (poly-d-fructose) from sucrose. These polymers are called homopolymers. Polymers containing more than one kind of monosaccharide are called heteropolymers.
The capsule contributes to the invasiveness of pathogenic bacteria—encapsulated cells are protected from phagocytosis unless they are coated with anticapsular antibody. The glycocalyx plays a role in the adherence of bacteria to surfaces in their environment, including the cells of plant and ani mal hosts. S mutans, for example, owes its capacity to adhere tightly to tooth enamel to its glycocalyx. Bacterial cells of the same or different species become entrapped in the glycocalyx, which forms the layer known as plaque on the tooth surface; acidic products excreted by these bacteria cause dental caries . The essential role of the glycocalyx in this process—and its formation from sucrose—explains the correlation of dental caries with sucrose consumption by the human population. Because outer polysaccharide layers bind a significant amount of water, the glycocalyx layer may also play a role in resistance to desiccation.
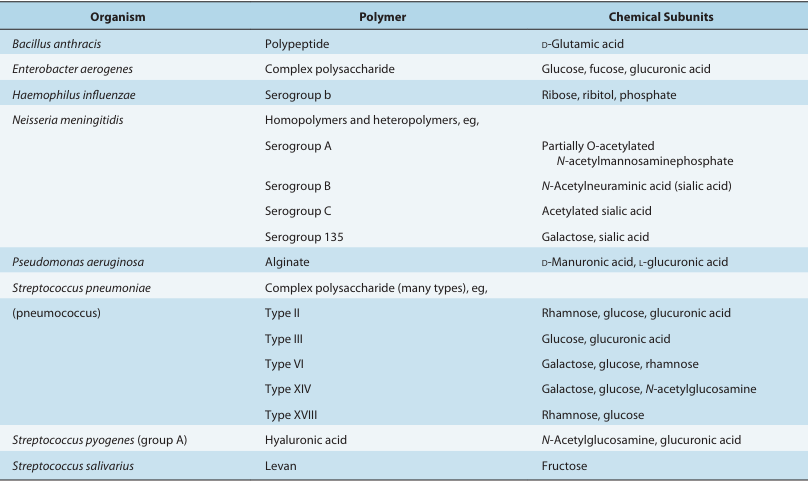
TABLE 1 Chemical Composition of the Extracellular Polymer in Selected Bacteria
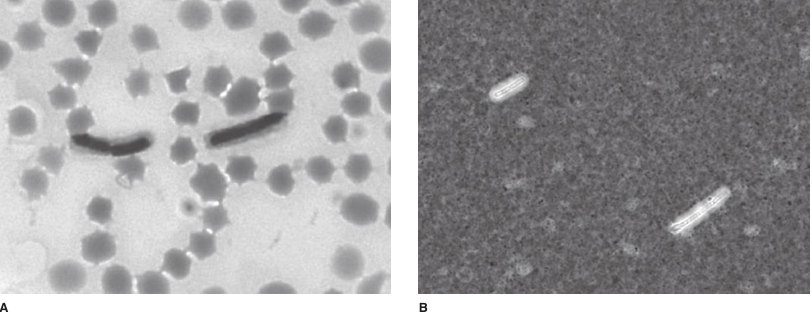
FIGURE 1- Bacterial capsules. A: Bacillus anthracis M’Faydean capsule stain, grown at 35°C, in defibrinated horse blood. B: Demonstration of the presence of a capsule in B anthracis by negative staining with India ink. This method is useful for improving visualization of encapsulated bacteria in clinical samples such as blood, blood culture bottles, or cerebrospinal fluid. (CDC, courtesy of Larry Stauffer, Oregon State Public Health Laboratory.)



|
|
|
|
علاج جفاف وتشقق القدمين.. مستحضرات لها نتائج فعالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
الإمارات.. تقنية رائدة لتحويل الميثان إلى غرافين وهيدروجين
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
سماحة السيد الصافي يؤكد دعم العتبة العباسية المقدسة للباحثين والحراك العلمي الذي يسهم في خدمة المجتمع
|
|
|