


 Grammar
Grammar
 Tenses
Tenses
 Present
Present
 Past
Past
 Future
Future
 Parts Of Speech
Parts Of Speech
 Nouns
Nouns
 Verbs
Verbs
 Adverbs
Adverbs
 Adjectives
Adjectives
 Pronouns
Pronouns
 Pre Position
Pre Position
 Preposition by function
Preposition by function 
 Preposition by construction
Preposition by construction
 Conjunctions
Conjunctions
 Interjections
Interjections
 Grammar Rules
Grammar Rules
 Linguistics
Linguistics
 Semantics
Semantics
 Pragmatics
Pragmatics
 Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension|
Read More
Date: 2024-01-03
Date: 2023-06-21
Date: 2023-09-09
|
affricate (n.)
A term used in the classification of CONSONANT sounds on the basis of their MANNER OF ARTICULATION: it refers to a sound made when the air-pressure behind a complete CLOSURE in the VOCAL TRACT is gradually released; the initial RELEASE produces a PLOSIVE, but the separation which follows is sufficiently slow to produce audible friction, and there is thus a FRICATIVE element in the sound also. However, the DURATION of the friction is usually not as long as would be the case of an independent fricative sound. If it is very brief indeed, the term affrication is used; in some English DIALECTS, such as Cockney, affricated plosives may be heard, such as [ts] and [dz], the auditory brevity of the friction element being indicated in the TRANSCRIPTION by the small symbols. It is, then, the combination of plosion and friction which identifies an affricate. In English, only [t] and [d] are released in this way, as in 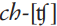 of chip and
of chip and 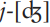 of just. German examples are [pf-] pfennig, ‘penny’ and [ts] zu, ‘to’.
of just. German examples are [pf-] pfennig, ‘penny’ and [ts] zu, ‘to’.
While affricates are PHONETICALLY easy to define, it is often a problem for PHONOLOGICAL analysis to decide whether a sequence of plosive and fricative elements constitutes a single functional unit, or is best analyzed as two separate units. English 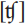 , for example, occurs initially, medially and finally in a word, readily contrasting with other PHONEMES, e.g. chip/sip, richer/ripper, patch/pat. On the other hand [tr], while occurring initially and medially (trip/sip, petrol/ petal), does not occur finally. Further, [tθ] only occurs finally (eighth/eight). Phonetically, all could be considered affricates; but, phonologically, there would be difference of opinion as to whether those with a restricted DISTRIBUTION could usefully be identified in this way.
, for example, occurs initially, medially and finally in a word, readily contrasting with other PHONEMES, e.g. chip/sip, richer/ripper, patch/pat. On the other hand [tr], while occurring initially and medially (trip/sip, petrol/ petal), does not occur finally. Further, [tθ] only occurs finally (eighth/eight). Phonetically, all could be considered affricates; but, phonologically, there would be difference of opinion as to whether those with a restricted DISTRIBUTION could usefully be identified in this way.
|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تستعد لإطلاق الحفل المركزي لتخرج طلبة الجامعات العراقية
|
|
|