


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 26-11-2021
Date: 18-11-2021
Date: 6-10-2021
|
Glycolysis Overview
The glycolytic pathway is used by all tissues for the oxidation of glucose to provide energy (as ATP) and intermediates for other metabolic pathways.
Glycolysis is at the hub of carbohydrate metabolism because virtually all sugars, whether arising from the diet or from catabolic reactions in the body, can ultimately be converted to glucose (Fig. 1A). Pyruvate is the end product of glycolysis in cells with mitochondria and an adequate supply of O2. This series of ten reactions is called aerobic glycolysis because O2 is required to reoxidize the NADH formed during the oxidation of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (Fig. 1B). Aerobic glycolysis sets the stage for the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, a major fuel of the TCA cycle. Alternatively, pyruvate is reduced to lactate as NADH is oxidized to NAD+ (Fig. 1C). This conversion of glucose to lactate is called anaerobic glycolysis because it can occur without the participation of O2.
Anaerobic glycolysis allows the production of ATP in tissues that lack mitochondria (for example, red blood cells [RBC] and parts of the eye) or in cells deprived of sufficient O2 (hypoxia).
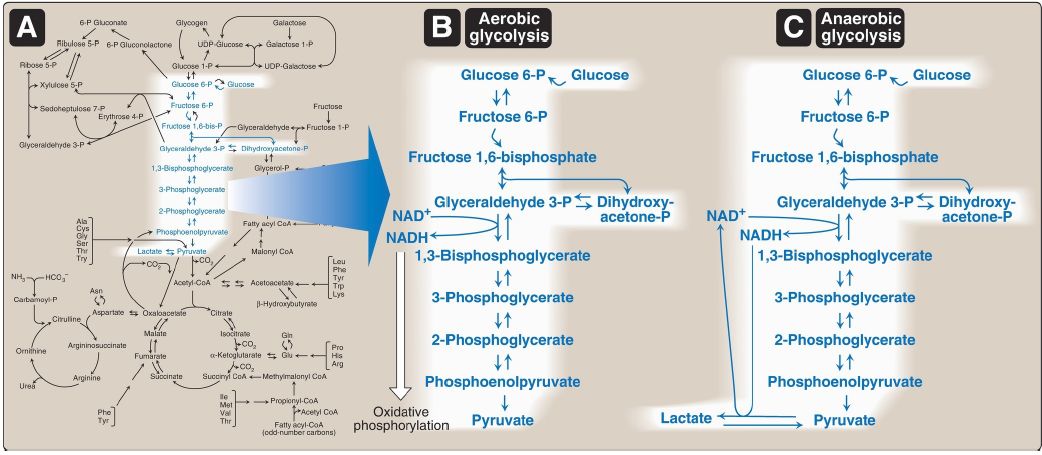
Figure 1: A. Glycolysis shown as one of the essential pathways of energy metabolism. B. Reactions of aerobic glycolysis. C. Reactions of anaerobic
glycolysis. NAD(H) = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; P = phosphate.



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تقدم دعوة إلى كلية مزايا الجامعة للمشاركة في حفل التخرج المركزي الخامس
|
|
|