


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 20-3-2016
Date: 26-12-2016
Date: 20-1-2021
|
Nonlinear Optics
Nonlinear optical effects are analyzed by considering the response of the dielectric material at the atomic level to the electric fields of an intense light beam. The propagation of a wave through a material produces changes in the spatial and temporal distribution of electrical charges as the electrons and atoms react to the electromagnetic fields of the wave. The main effect of the forces exerted by the fields on the charged particles is a displacement of the valence electrons from their normal orbits. This perturbation creates electric dipoles whose macroscopic manifestation is the polarization. For small field strengths this polarization is proportional to the electric field. In the nonlinear case, the reradiation comes from dipoles whose amplitudes do not faithfully reproduce the sinusoidal electric field that generates them. As a result, the distorted reradiated wave contains different frequencies from that of the original wave.
On a microscopic scale, the nonlinear optical effect is rather small even at relatively high-intensity levels, as the following example illustrates.We will compare the applied electric field strength of a high-intensity beam to the atomic electric field which binds the electrons to the nucleus. The magnitude of the atomic field strength is approximately equal to Eat = e/4π∈0r 2 where e is the charge of an electron, ∈0 is the permitivity of free space, and r is the radius of the electron orbit. With r = 10−8 cm one obtains Eat = 109 V/cm. A laser beam with a power density of I = 100MW/cm2 generates an electric field strength in the material of about E = 105 V/cm according to I = n0E2(μ0/∈0)−1/2, where n0 is the refractive index and (μ0/∈0)1/2 is the impedance of free space. To observe such a small effect, which is on the order of 10−4, it is important that the waves add coherently on a macroscopic scale. This requires that the phase velocities of the generated wave and the incident wave are matched.
In a given material, the magnitude of the induced polarization per unit volume P will depend on the magnitude of the applied electric field E. We can therefore expand P in a series of powers of E and write
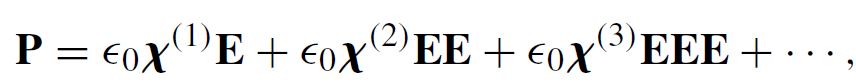 .........(1)
.........(1)
where ∈0 is the permitivity of free space and χ(1) is the linear susceptibility representing the linear response of the material. The two lowest-order nonlinear responses are accounted for by the second- and third-order nonlinear susceptibilities χ(2) and χ(3). The expression of the polarization in anisotropy materials is rather complicated, for the induced polarization depends not only on the magnitude of the electric vector but on the magnitude and direction of all vectors that characterize the electromagnetic field. Normally χ(1) >> χ(2) >> χ(3) and therefore the nonlinear effects will be negligible unless the electric field strength is very high.
The linear term in (1) represents three separate equations, one for each value of the i th Cartesian coordinate of P, that is,
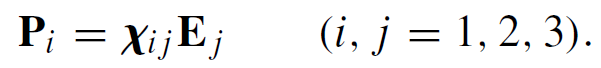 ..........(2)
..........(2)
The linear polarization tensor, which is rank 2, has an array of nine coefficients. The linear susceptibility, related to the refractive index through χ = n20−1 and to the dielectric constant ∈ = ∈0(1 +χ), is responsible for the linear optical properties of the medium such as refraction, dispersion, absorption, and birefringence. In the linear regime optical properties are independent of light intensity and the wavelength of radiation does not change.
The nonlinear optical susceptibilities of second and third order which describe three- and four-wave mixing processes, respectively, give rise to a large variety of optical phenomena since each electric field can have a different frequency, propagation vector, polarization, and relative phase. Therefore P can contain many different product terms of the various interacting fields. In the following overview only interactions that are utilized in the nonlinear devices described in the remainder of this chapter are described.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|