


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 21-3-2016
Date: 9-11-2020
Date: 10-11-2020
|
CERENKOV RADIATION
We saw that nothing, not even information, could travel faster than the speed of light. If it did, we could, for example, get answers to questions that had not yet been thought of. When moving through a medium, the speed of a light wave is slowed by repeated scattering and it is no longer true that nothing can move faster than the speed of light in that medium. We saw for example that the speed of light in water is only 3/4 the speed c in vacuum. Many elementary particles, like the muons in the muon lifetime experiment, travel at speeds much closer to c. When a charged particle moves faster than the speed of light in a medium, we get an effect not unlike the sonic boom produced by a supersonic jet. We get a shock wave of light that is similar to a sound shock wave (sonic boom), or to the water shock wave shown in Figure (1) reproduced here. The light shock wave is called Cerenkov radiation after the Russian physicist Pavel Cerenkov who received the 1958 Nobel prize for discovering the effect.
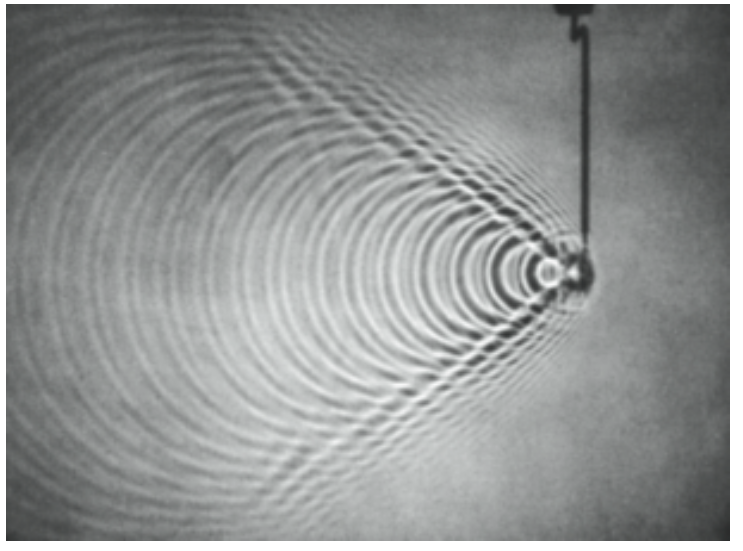
Figure 1: When the source of the waves moves faster than the speed of the waves, the wave fronts pile up to produce a shock wave as shown. This shock wave is the sonic boom you hear when a jet plane flies overhead faster than the speed of sound.
In the muon lifetime picture, one observed how long muons lived when stopped in a block of plastic. The experiment was made possible by Cerenkov radiation. The muons that stopped in the plastic, entered moving faster than the speed of light in plastic, and as a result emitted a flash of light in the form of Cerenkov radiation. When the muon decayed, a charged positron and a neutral neutrino were emitted. In most cases the charged positron emerged faster than the speed of light in the plastic, and also emitted Cerenkov radiation. The two flashes of light were detected by the phototube which converted the light flashes to voltage pulses. The voltage pulses were then displayed on an oscilloscope screen where the time interval between the pulses could be measured. This interval represented the time that the muon lived, mostly at rest, in the plastic.



|
|
|
|
لخفض ضغط الدم.. دراسة تحدد "تمارين مهمة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
طال انتظارها.. ميزة جديدة من "واتساب" تعزز الخصوصية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مشاتل الكفيل تزيّن مجمّع أبي الفضل العبّاس (عليه السلام) بالورد استعدادًا لحفل التخرج المركزي
|
|
|