


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 18-8-2020
Date: 28-7-2020
Date: 28-7-2020
|
Observational radio astronomy: Observing the Sun
The microwave output from the Sun consists of broad-band noise (or ‘hiss’ when converted to an audio signal) generated by the thermal motions of electrons in the Sun’s atmosphere. At microwave frequencies, most of the radiation results from the long wavelength tail of the Sun’s black body spectrum.
The telescope has a beam relating to the angular extent of the patch on the sky that it sees at any one time. To estimate the beamwidth, consider it corresponding to the diffraction limit given by the aperture of the telescope. If we take D = 55 cm and the wavelength, λ, to be 3 cm, then the beamwidth is
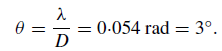
Any black body object that fills the beam will produce a signal which depends only on its temperature (not on its composition, distance, size, etc). This fact can be used to estimate the temperature of the Sun.
Any object that occupies only a fraction of the beamwidth will appear to have a temperature that is reduced by that same fraction. The Sun, with an angular diameter of about 1/2◦, does not fill the beamwidth of the telescope and the temperature derived from the immediate output signal needs to be scaled. For the equipment used here, the scaling factor is given by
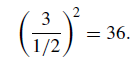
Microwaves pass through cloud quite well and, consequently, the experiment can be undertaken in overcast conditions, even when the Sun is obscured. According to the local time, an estimate of the
azimuth of the Sun may be calculated making it easier to locate its direction. Adjust the pointing of the dish and the sensitivity of the power meter until a maximum output is achieved. From this position, any slight movement of the dish in any direction will cause the signal to drop. Record the azimuth and altitude of the Sun and note the time at which the measurement was made.
Drop the altitude of the telescope to < 0◦ (i.e. aim at the ground). The meter deflection should be similar to that corresponding to the Sun. Although the ground is only about 290 K, it ‘fills the beam’. Using the scaling factor as outlined earlier, estimate the temperature of the Sun.



|
|
|
|
لخفض ضغط الدم.. دراسة تحدد "تمارين مهمة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
طال انتظارها.. ميزة جديدة من "واتساب" تعزز الخصوصية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مشاتل الكفيل تزيّن مجمّع أبي الفضل العبّاس (عليه السلام) بالورد استعدادًا لحفل التخرج المركزي
|
|
|