


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 12-8-2020
Date: 24-2-2016
Date: 8-9-2020
|
The Sun as a timekeeper: A horizontal sundial
As the name implies, a horizontal sundial is designed so that the shadow cast by the style falls on to a horizontal surface (see figure 1). In order that the shadow line should be distinct, the style should be thin, of the order of 1 mm. It should be cut so that the angle which it makes with a horizontal plane is equal to the latitude of the location. When positioned correctly on the meridian the line of the style should point to the north celestial pole.
The markings to be inscribed on the plane to correspond to the hour lines may be drawn by applying the equation
tan γ = sin ∅ tan h
where γ is the angle between the noon-line and the edge of the shadow corresponding to time, h (converted to degrees), the angle by which the Sun is away from the meridian, and ∅ is the latitude. Obviously, at noon, h is equal to zero.
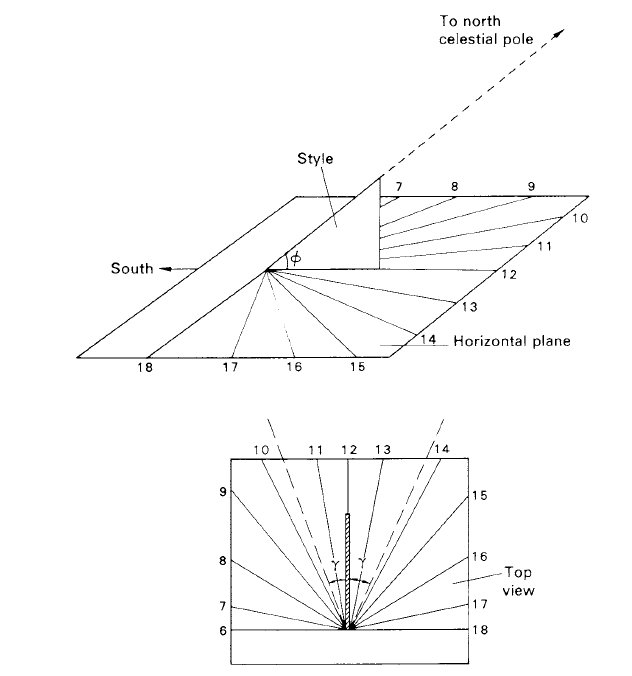
Figure 1. A horizontal sundial.
As an example, the value of γ is calculated for the times when the Sun is 2 hr (h = 30◦) either side of the meridian, i.e. at 10 hr and 14 hr for a latitude ∅ = 55◦ 53'.
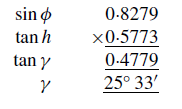
For this situation, γ is equal to 25◦ 33'. To complete the sundial, values of γ should be calculated and
drawn, say for each 10 minute interval. In setting the dial, it is necessary to fix the marked plane horizontal and this can be done easily using a spirit level. The setting of the noon-line can be achieved by rotating the dial by small amounts each day until on any one day, the observed angle γ is equal on both sides of noon for equal time intervals either side of noon, say 2 hr.



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تستعد لإطلاق الحفل المركزي لتخرج طلبة الجامعات العراقية
|
|
|