


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 30-12-2020
Date: 18-8-2020
Date: 7-8-2020
|
Image photometry: CCD photometry
As a result of the high quantum efficiency of these devices and their linearity of response to light, CCDs have excellent scope for undertaking differential photometry of stars. Unlike photometry using a photomultiplier, which is, of course, also differential in that target stars and standard stars are observed in a cyclic sequence, CCD measurements require the target and standard object to be in the same field of view covered by the chip. Because of the small area of the detector, this can sometimes be a restriction not usually encountered in photography. Unlike the photographic process, however, there is virtually no delay in obtaining the data as each picture or frame is read directly into a computer with the potential of fast analysis of the images.
When stellar photometry is being undertaken, the required differential measurements are best obtained if the targets and calibration stars are in the same field covered by the chip so that the required information is contained in one individual frame. In determining the brightness values, one star is selected to determine the point spread function (PSF), so exploring the way by which a would-be point image is spread by the seeing conditions during the exposure. Using the determined constants associated with the particular PSF of the individual frame, the function is fitted to the intensity distributions of the other stellar images and the appropriate magnitude values are assigned from which magnitude differences between the various stars can then be calculated. This is done using a suite of software. The process is fairly automatic requiring the minimum of keyboard interaction. Star images can be searched for automatically with the centroid of their positions given in terms of the pixel position by row and column numbers. Photometric accuracies better than ±0·01 are readily achieved according to the number of photons that are accumulated within the point spread function.
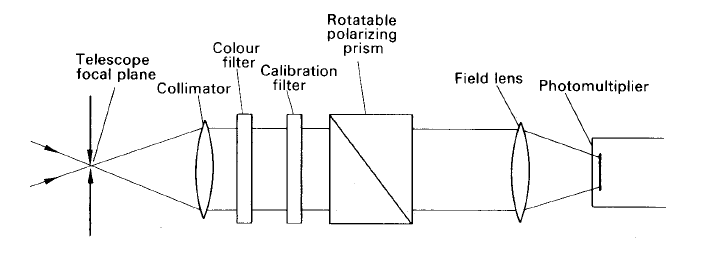
Figure 1. A single-beam polarimeter.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مركز الصادقين يعقد ندوته العلمية الثالثة عن دور علماء الشيعة في تطور العلوم
|
|
|