


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 31-8-2020
Date: 5-8-2020
Date: 1-9-2020
|
Stellar parallax: Stellar parallactic movements
The direction of a star as seen from the Earth is not the same as the direction when viewed by a hypothetical observer at the Sun’s centre. As the Earth moves in its yearly orbit round the Sun, the geocentric direction (the star’s position on a geocentric celestial sphere) changes and traces out what is termed the parallactic ellipse. Thus, in figure 1, the star X at a distance d kilometres is seen from the Earth at E1 to lie in the direction E1X1 relative to the heliocentric direction SX'. Six months later, the Earth is now at the point E2 in its orbit and the geocentric direction of the star is E2X2.
The concepts used in stellar parallax are analogous to those used in geocentric parallax. Thus, if we looked upon the Earth’s orbital radius a as the base-line, we can define the star’s parallax as P, given by
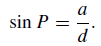 .........(1)
.........(1)
Because stellar distances are so great compared with the Earth’s orbital radius, we can assume that the Earth’s orbit to be circular. Angle P is small so that we can write equation (1) as

where P is in seconds of arc.
Again, if we draw E1Y parallel to SX in figure 1. and let ∠Y E1X = ∠E1XS = p, we have, from ΔE1XS,
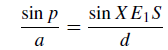
or
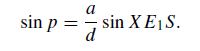
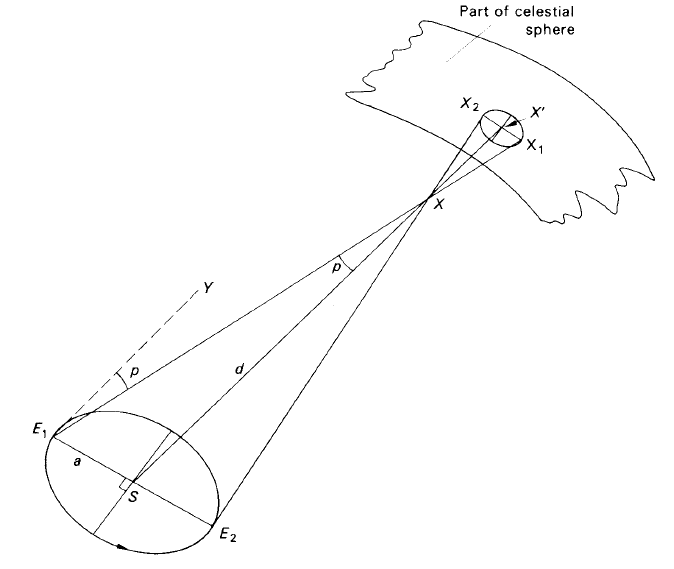
Figure 1. The parallactic ellipse (the size is exaggerated for clarity).
Using equation (1) and letting ∠XE1S = θ, we obtain
sin p = sin P sin θ
or
p = P sin θ (2)
since both p and P are small angles.
Thus, the star is displaced towards the Sun along the great circle through the star’s heliocentric position and the Sun by an amount p, given by equation (2), where P is the star’s parallax and θ is the angle between the Sun’s direction and the star’s. Whereas P remains constant, p and θ vary because of the Earth’s movement in its orbit about the Sun.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|