

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
General Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
18-10-2019
1643
General Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds
- aldol reaction
- alkylation
- alpha substitution
- carbonyl condensation
- enol
- enolate anion
- nucleophilic acyl substitution
- nucleophilic addition reaction
A “nucleophilic addition reaction” (of a carbonyl compound) involves the initial attack of a nucleophile on the slightly positive carbonyl‑carbon atom to form a tetrahedral intermediate.
In a “nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction,” a nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon of a carboxylic acid derivative
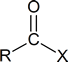
and initially produces a tetrahedral intermediate. The intermediate then reacts by expelling the leaving group, X, thereby forming a new carboxylic acid derivative.
In an “alpha substitution reaction” of a carbonyl compound, one of the hydrogen atoms attached to a carbon atom adjacent to the carbonyl group is removed and replaced by some other group.
Alpha substitution reactions of carbonyl compounds involve the “enol” form of the compound. Keto‑enol tautomerism was briefly introduced in Section 9.4. Review this section if necessary.
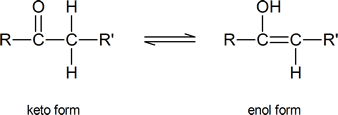
As you can see from the above diagram, the enol form has a hydroxyl group attached to one of the s p2 ‑hybridized carbon atoms of a carbon‑carbon double bond. Removal of the proton from the hydroxyl group produces a resonance‑stabilized “enolate anion”:
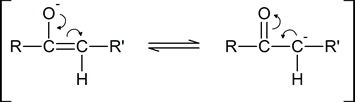
A “carbonyl condensation reaction” is one in which two carbonyl‑ containing molecules condense together (i.e., join together), often with the elimination of water. The reaction involves the formation of an enolate anion from one carbonyl‑containing molecule, followed by the subsequent nucleophilic attack by this enolate anion on the carbonyl carbon atom of the second molecule.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















