
Structures of the 13 group elements
 المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
 المصدر:
Inorganic Chemistry
المصدر:
Inorganic Chemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 300
الجزء والصفحة:
p 300
 28-1-2018
28-1-2018
 1510
1510
Structures of the 13 group elements
The first ‘allotrope’ of boron to be documented was the a-tetragonal form, but this has been reformulated as a carbide or nitride, B50C2 or B50N2, the presence of C or N arising as a result of synthetic conditions.
This carbidic phase is not the same as the boron carbide B4C (more correctly formulated as B13C2)
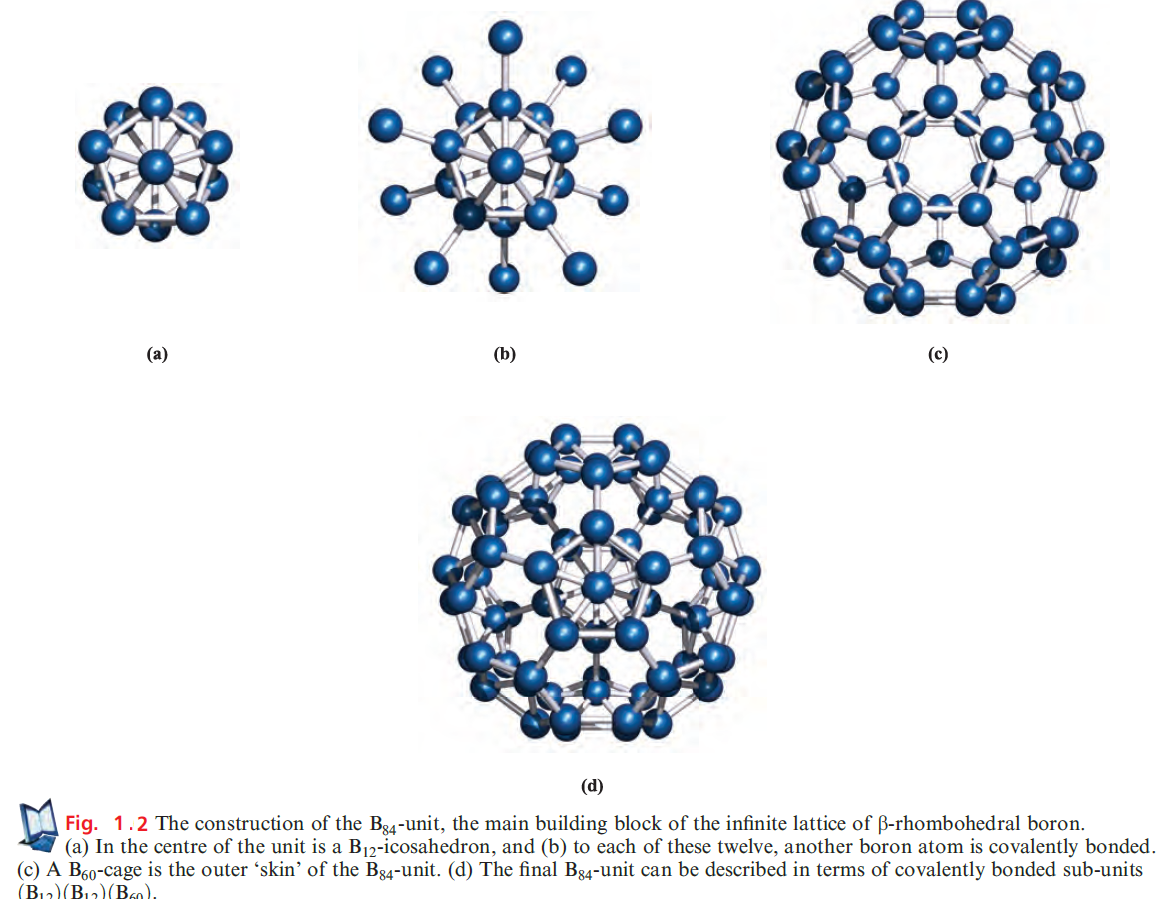
which has a structure related to that of β-rhombohedral B. The standard state of B is the b-rhombohedral form, but the structure of α-rhombohedral B makes an easier starting point in our discussion. Both the α- and β-rhombohedral allotropes contain icosahedral B12-units (Figures 1.1 and 1.2a); the bonding in elemental B is covalent, and within each B12-unit, it is delocalized. We return to bonding descriptions in boron cluster compounds but for now note that the connectivity of each B atom in Figures 1.1 and 1.2 exceeds the number of valence electrons available per B.
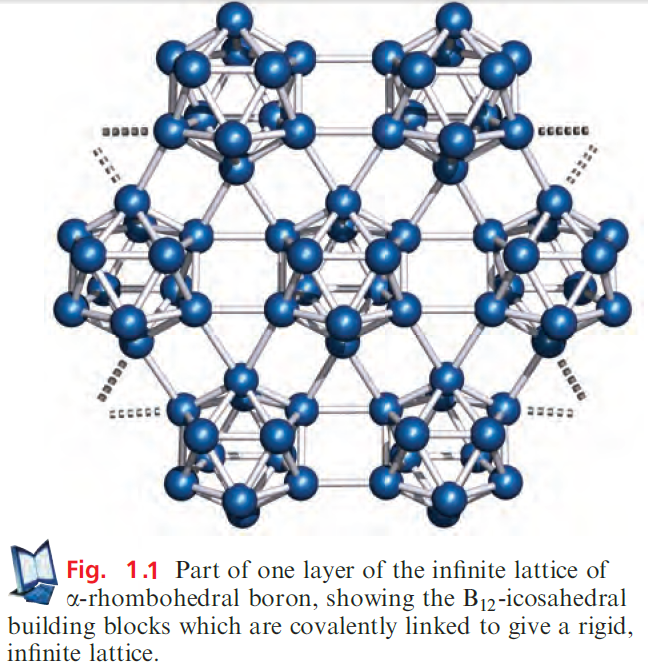
α-Rhombohedral boron consists of B12-icosahedra covalently linked by B_B bonds to form an infinite lattice. A readily interpretable picture of the lattice is to consider each icosahedron as an approximate sphere, and the overall structure as a ccp array of B12-icosahedra, one layer of which is shown in Figure 1.1.
The structure of β-rhombohedral B consists of B84-units, connected through B10-units. Each B84-unit is conveniently viewed in terms of the subunits shown in Figure 1.2; their interrelationship is described in the figure caption, but an interesting point to note is the structural relationship between the B60-subunit shown in Figure 1.2c and the fullerene C60. The covalent lattices of both aand β-rhombohedral B are extremely rigid, making crystalline B very hard, with a high melting point (2453K for β-rhombohedral B).
 الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


