
Xenon-135 Response to Reactor Shutdown
 المؤلف:
U.S. Department of Commerce, National Technical Information Service, 1993
المؤلف:
U.S. Department of Commerce, National Technical Information Service, 1993
 المصدر:
The Nuclear Physics and Reactor Theory Handbook
المصدر:
The Nuclear Physics and Reactor Theory Handbook
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 35
الجزء والصفحة:
p 35
 21-4-2017
21-4-2017
 2718
2718
Xenon-135 Response to Reactor Shutdown
When a reactor is shutdown, the neutron flux is reduced essentially to zero. Therefore, after shutdown, xenon-135 is no longer produced by fission and is no longer removed by burnup. The only remaining production mechanism is the decay of the iodine-135 which was in the core at the time of shutdown. The only removal mechanism for xenon-135 is decay.
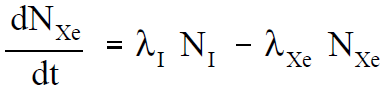
Because the decay rate of iodine-135 is faster than the decay rate of xenon-135, the xenon concentration builds to a peak. The peak is reached when the product of the terms λ1N1 is equal to λXeNXe (in about 10 to 11 hours). Subsequently, the production from iodine decay is less than the removal of xenon by decay, and the concentration of xenon-135 decreases. The greater the flux level prior to shutdown, the greater the concentration of iodine-135 at shutdown; therefore, the greater the peak in xenon-135 concentration after shutdown. This phenomenon can be seen in Figure 1, which illustrates the negative reactivity value of xenon-135 following shutdown from various neutron flux levels.
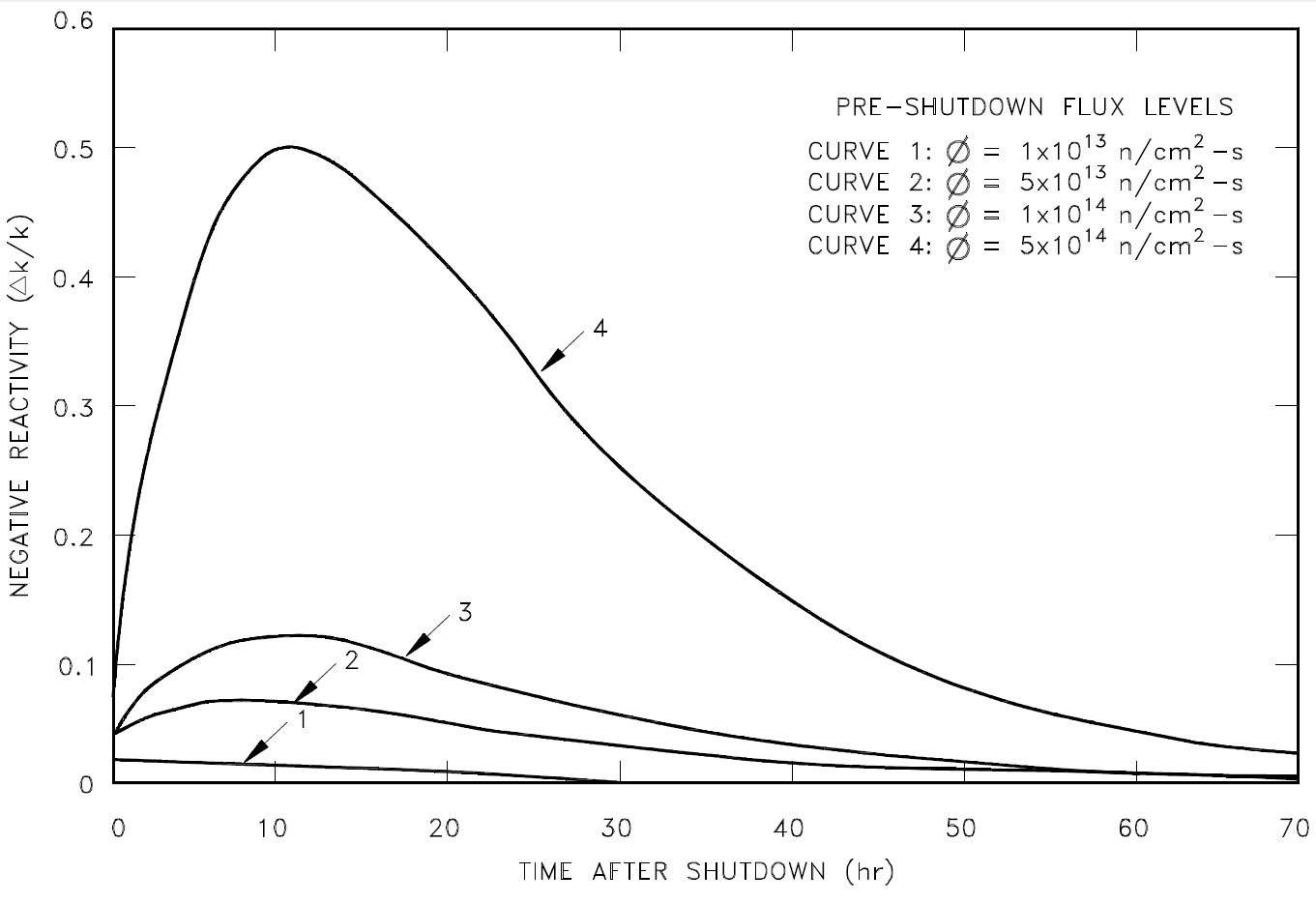
Figure 1: Xenon-135 Reactivity After Reactor Shutdown
Negative xenon reactivity, also called xenon poisoning, may provide sufficient negative reactivity to make the reactor inoperable because there is insufficient positive reactivity available from control rod removal or chemical shim dilution (if used) to counteract it. The inability of the reactor to be started due to the effects of xenon is sometimes referred to as a xenon precluded startup. The period of time where the reactor is unable to "override" the effects of xenon is called xenon dead time. Because the amount of excess core reactivity available to override the negative reactivity of the xenon is usually less than 10% Δk/k, thermal power reactors are normally limited to flux levels of about 5 x 1013 neutrons/cm2-sec so that timely restart can be ensured after shutdown. For reactors with very low thermal flux levels (~5 x 1012 neutrons/cm2-sec or less), most xenon is removed by decay as opposed to neutron absorption. For these cases, reactor shutdown does not cause any xenon-135 peaking effect.
Following the peak in xenon-135 concentration about 10 hours after shutdown, the xenon-135 concentration will decrease at a rate controlled by the decay of iodine-135 into xenon-135 and the decay rate of xenon-135. For some reactors, the xenon-135 concentration about 20 hours after shutdown from full power will be the same as the equilibrium xenon-135 concentration at full power. About 3 days after shutdown, the xenon-135 concentration will have decreased to a small percentage of its pre-shutdown level, and the reactor can be assumed to be xenon free without a significant error introduced into reactivity calculations.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


