
Hydrides of The group 14 elements
 المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
 المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 الجزء والصفحة:
2th ed p 354
الجزء والصفحة:
2th ed p 354
 28-3-2017
28-3-2017
 2107
2107
Hydrides of The group 14 elements
Although the extensive chemistry of hydrocarbons (i.e. carbon hydrides) lies outside this book, we note several points for comparisons with later group 14 hydrides:
• Table 1.1 illustrated the relative strength of a C_H bond compared with C_Cl and C_O bonds, and this trend is not mirrored by later elements;
- CH4 is chlorinated with some difficulty, whereas SiH4 reacts violently with Cl2;
- CH4 is stable with respect to hydrolysis, but SiH4 is readily attacked by water;
- SiH4 is spontaneously inflammable in air and, although it is the kinetic stability of CH4 with respect to reaction with O2 at 298K that is crucial, values of ΔcHo show that combustion of SiH4 is more exothermic than that of CH4;
- catenation is more common for C than the later group 14 elements, and hydrocarbon families are much more diverse than their Si, Ge, Sn and Pb analogues.
Table 1.1 Some experimental covalent bond enthalpy terms (kJ mol�-1); the values for single bonds refer to the group 14 elements in tetrahedral environments.
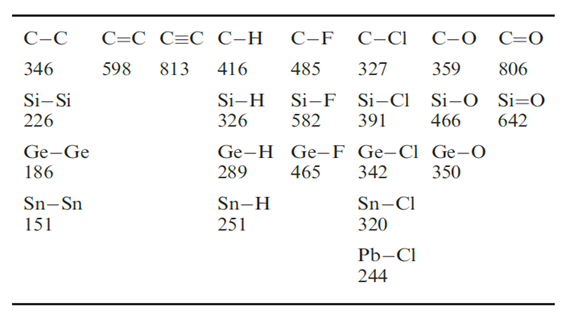
Worked example 13.3 Bond enthalpies and group 14 hydrides
Suggest why catenation is more common for C than for Si, Ge and Sn. Why is this relevant to the formation of families of saturated hydrocarbon molecules?
The much higher C_C bond enthalpies (see Table 1.1) compared with those of Si_Si, Ge_Ge and Sn_Sn bonds means that the formation of compounds containing bonds between carbon atoms is thermodynamically more favourable than analogous compounds containing Si_Si, Ge_Ge and Sn_Sn bonds. On descending group 14, orbital overlap becomes less efficient as the valence orbitals become more diffuse, i.e. as the principal quantum number increases. The backbones of saturated hydrocarbons are composed of C_C bonds, i.e. their formation depends on catenation being favourable. An additional factor that favours the formation of hydrocarbons is the strength of the C_H bonds (stronger than Si_H, Ge_H or Sn_H (see Table 1.1). On descending group 14, the hydrides become thermodynamically less stable, and the kinetic barriers to reactions such as hydrolysis of E_H bonds become lower.a
 الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


