
Nuclides
 المؤلف:
U.S. Department of Commerce, National Technical Information Service, 1993
المؤلف:
U.S. Department of Commerce, National Technical Information Service, 1993
 المصدر:
The Nuclear Physics and Reactor Theory Handbook
المصدر:
The Nuclear Physics and Reactor Theory Handbook
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 4
الجزء والصفحة:
p 4
 25-3-2017
25-3-2017
 2659
2659
Nuclides
The total number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus. The number of neutrons in a nucleus is known as the neutron number and is given the symbol N. The mass number of the nucleus is the total number of nucleons, that is, protons and neutrons in the nucleus. The mass number is given the symbol A and can be found by the equation Z + N = A.
Each of the chemical elements has a unique atomic number because the atoms of different elements contain a different number of protons. The atomic number of an atom identifies the particular element.
Each type of atom that contains a unique combination of protons and neutrons is called a nuclide. Not all combinations of numbers of protons and neutrons are possible, but about 2500 specific nuclides with unique combinations of neutrons and protons have been identified. Each nuclide is denoted by the chemical symbol of the element with the atomic number written as a subscript and the mass number written as a superscript, as shown in Figure 1. Because each element has a unique name, chemical symbol, and atomic number, only one of the three is necessary to identify the element. For this reason nuclides can also be identified by either the chemical name or the chemical symbol followed by the mass number (for example, U-235 or uranium-235). Another common format is to use the abbreviation of the chemical element with the mass number superscripted (for example, 235U). In this handbook the format used in the text will usually be the element's name followed by the mass number. In equations and tables, the format in Figure 1 will usually be used.
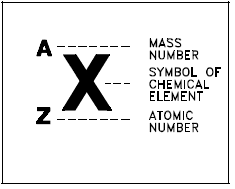
Figure 1: Nomenclature for Identifying Nuclides
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


