
Homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts
 المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
 المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
 الجزء والصفحة:
694
الجزء والصفحة:
694
 2025-10-16
2025-10-16
 381
381
Homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts
Key points: Homogeneous catalysts are present in the same phase as the reagents, and are often well defined; heterogeneous catalysts are present in a different phase from the reagents. Catalysts are classified as homogeneous if they are present in the same phase as the reagents; this normally means that they are present as solutes in liquid reaction mixtures. Catalysts are heterogeneous if they are present in a different phase from that of the reactants; this normally means that they are present as solids with the reactants present either as gases or in solution. Both types of catalysis are discussed in this chapter and will be seen to be fundamentally similar. From a practical standpoint, homogeneous catalysis is attractive because it is often highly selective towards the formation of a desired product. In large-scale industrial processes, homogeneous catalysts are preferred for exothermic reactions because it is easier to dissipate heat from a solution than from the solid bed of a heterogeneous catalyst. In principle, every homogeneous catalyst molecule in solution is accessible to reagents, potentially leading to very high activities. It should also be borne in mind that the mechanism of homogeneous catalysis is more accessible to detailed investigation than that of heterogeneous catalysis as species in solution are often easier to characterize than those on a surface and because the interpretation of rate data is frequently easier. The major disadvantage of homogeneous catalysts is that a separation step is required. Heterogeneous catalysts are used very extensively in industry and have a much greater economic impact than homogeneous catalysts. One attractive feature is that many of these solid catalysts are robust at high temperatures and therefore tolerate a wide range of operating conditions. Reactions are faster at high temperatures, so at high temperatures solid catalysts generally produce higher outputs for a given amount of catalyst and reaction time than homogeneous catalysts operating at lower temperatures in solutions. Another reason for their widespread use is that extra steps are not needed to separate the product from the catalyst, resulting in efficient and more environmentally friendly processes. Typically, gaseous or liquid reactants enter a tubular reactor at one end, pass over a bed of the catalyst, and products are collected at the other end. This same simplicity of design applies
to the catalytic converter used to oxidize CO and hydrocarbons and reduce nitrogen oxides in automobile exhausts (Fig. 26.4), see also Box 26.1.
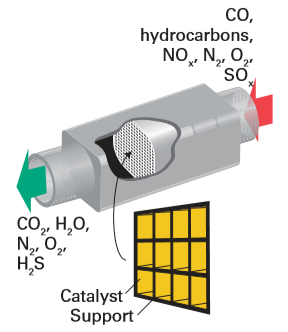
Figure 26.4 A heterogeneous catalyst in action. The automobile catalytic converter oxidizes CO and hydrocarbons, and reduces nitrogen and sulfur oxides. The particles of a metal catalyst are supported on a robust, ceramic honeycomb.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


